E‑commerce in manufacturing is changing how businesses work, especially small and medium-sized ones. It connects production with customer needs by making it easier to manage sales, track inventory, and automate business processes in manufacturing.
With e‑commerce manufacturing companies can reach more customers and grow faster. It’s not just about selling products online; manufacturing e‑commerce helps improve the supply chain, reduce manual tasks, and offer better customer service. As technology improves, more manufacturers see the benefits of using b2b manufacturing ecommerce to make their operations more efficient and modern.
- Understanding E‑Commerce in the Manufacturing Industry
- Key Types of E‑Commerce Models for Manufacturers
- How E‑Commerce Transforms Business Processes in Manufacturing
- Steps to Implement E‑Commerce for Manufacturing SMEs
- Challenges and Opportunities of E‑Commerce in Manufacturing
- Frequently Asked Questions on E‑Commerce in Manufacturing
Understanding E‑Commerce in the Manufacturing Industry
E‑commerce has transformed how manufacturers operate, offering tools to improve efficiency and reach. It bridges traditional production methods with modern digital platforms, helping businesses adapt to changing demands and customer expectations.
What is E‑Commerce in Manufacturing?
E‑commerce in manufacturing means using online platforms and digital tools to simplify business operations. It helps manufacturers sell products, manage orders, and connect with buyers efficiently. This process often involves b2b ecommerce for manufacturers, where businesses sell to other companies instead of individual customers.
The application of e‑commerce in the manufacturing sector goes beyond online stores. It includes integrating supply chain systems, enabling online bulk ordering, and automating routine tasks to save time and reduce errors.
Key Differences Between Retail and Manufacturing E‑Commerce
Retail e‑commerce typically serves individual consumers with smaller, one-time purchases. On the other hand, manufacturing e‑commerce is about meeting the needs of business buyers.
- Order Volume: Manufacturing deals with bulk purchases instead of single items.
- Contracts: Long-term agreements are common, unlike retail’s one-off sales.
- Customization: Manufacturers may adjust product features to meet buyer requirements.
- Pricing: Negotiations and tiered pricing structures are more common than fixed prices.
This focus on B2B interactions allows e‑commerce manufacturers to build stronger partnerships and provide tailored solutions for buyers.
Benefits of E‑Commerce for Manufacturing SMEs
Small and medium-sized manufacturers can greatly benefit from e‑commerce:
- Cost Savings: Digital tools lower operating costs by reducing paperwork and manual processes.
- Market Expansion: SMEs can reach global buyers without the need for physical presence.
- Process Automation: Automating business processes in manufacturing ensures smoother workflows and fewer delays.
- Data Insights: Online platforms offer detailed analytics to understand customer needs and improve services.
By adopting ecommerce applications in manufacturing, SMEs can grow faster, serve customers better, and compete effectively in modern markets.
We have been using Kladana since March 2011, it’s an excellent solution!
After we tried the free version, we noticed that synchronization with the online store that we wanted to use is available. Then we tried the barcode scanners and they worked well. That is how we made a choice in favor of Kladana.
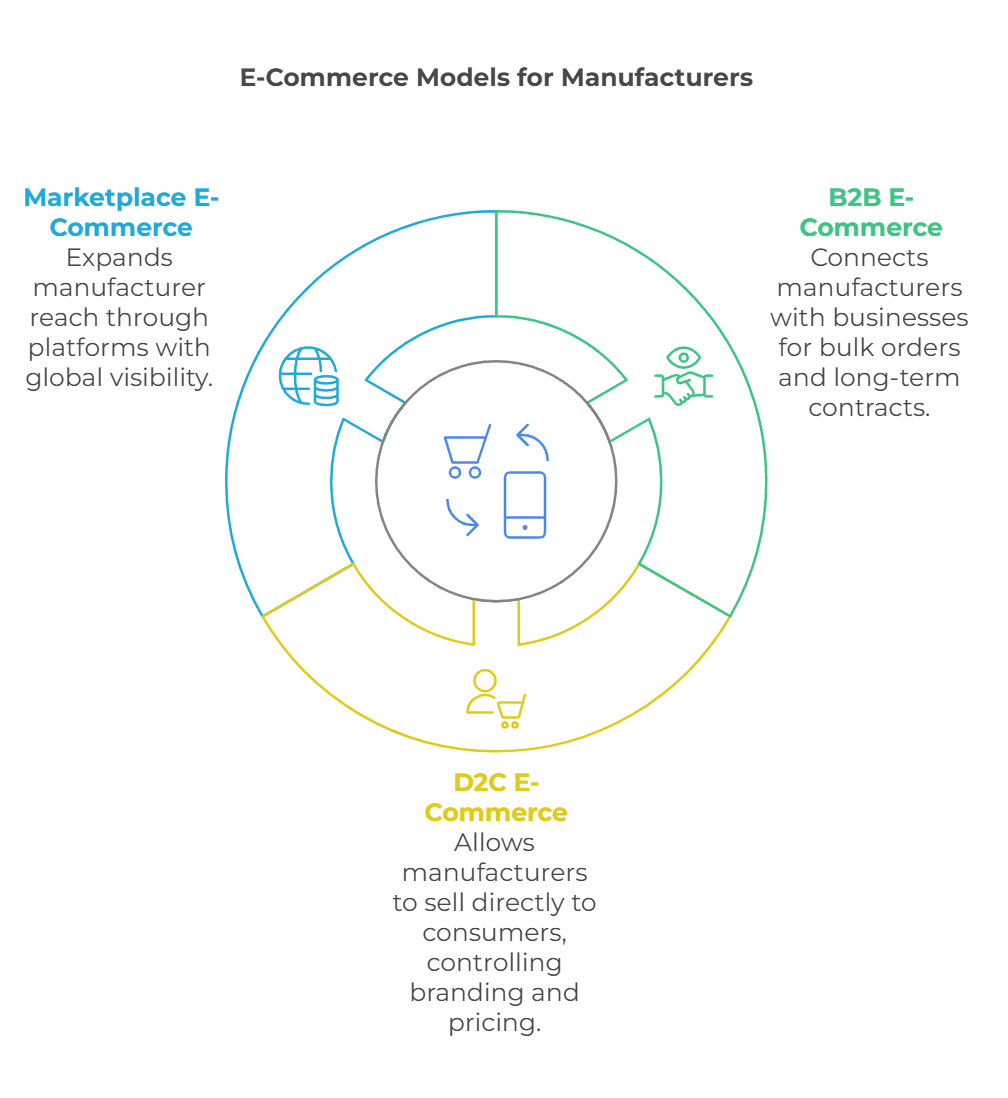
Key Types of E‑Commerce Models for Manufacturers
Different e‑commerce applications in manufacturing models cater to diverse business goals. Here are three key types that manufacturers can use:
Business-to-Business (B2B) E‑Commerce
B2b manufacturing e‑commerce connects manufacturers with wholesalers, retailers, and other businesses.
- Manufacturers handle bulk orders and set custom pricing for different buyers.
- These platforms focus on long-term contracts, ensuring steady demand and repeat business.
- Features like automated reordering, credit terms, and buyer-specific catalogs make operations more efficient.
Adopting b2b e‑commerce for manufacturers supports streamlined transactions and builds strong partnerships.
Direct-to-Consumer (D2C) E‑Commerce
D2C e‑commerce allows manufacturers to sell directly to customers, bypassing intermediaries.
- By launching their own websites, e‑commerce manufacturers control branding, pricing, and customer experience.
- This model enables better profit margins and faster response to market demands.
- Manufacturers can engage directly with buyers, gather feedback, and offer personalized deals.
For many, D2C is a way to test new products or expand into new markets.
Marketplace E‑Commerce
Marketplace platforms help manufacturers reach a wider audience.
- These platforms provide visibility and access to global buyers.
- Manufacturers can list their products without investing in a standalone e‑commerce website.
- Built-in tools for advertising and analytics make it easier to manage sales performance.
This model is ideal for manufacturers looking to scale their operations or explore e‑commerce in the manufacturing industry with minimal risk.
Each type of e‑commerce serves a unique purpose, and businesses often combine models to maximize results.
How E‑Commerce Transforms Business Processes in Manufacturing
E‑commerce has a significant impact on business processes in manufacturing. It simplifies operations and helps companies grow more efficiently.
Streamlining Supply Chain Management
E‑commerce for manufacturing businesses can greatly improve supply chain management.
- Digital platforms allow manufacturers to automate procurement and vendor management.
- Suppliers, inventory, and orders are tracked in real time, reducing errors and delays.
- Manufacturers can coordinate logistics more efficiently, ensuring timely deliveries.
This leads to faster operations and lower costs, which benefits manufacturers in highly competitive markets.
Improving Decision-Making with Data Analytics
The e‑commerce application in manufacturing provides manufacturers with valuable data.
- Data on sales trends, customer behavior, and inventory levels is readily available.
- Analytics tools help manufacturers make informed decisions based on this data.
- By identifying patterns, companies can adjust production schedules and forecast demand more accurately.
These insights improve overall decision-making and help businesses stay ahead of the competition.
Scaling Operations Without Infrastructure Constraints
One of the key advantages of manufacturing e‑commerce is the ability to scale without heavy infrastructure costs.
- Digital platforms allow manufacturers to grow their businesses without investing in large physical spaces or additional employees.
- Cloud-based solutions ensure that even small manufacturers can access enterprise-level tools.
- By automating routine tasks, companies can manage more orders without needing more resources.
This flexibility allows manufacturing companies to expand quickly and efficiently.
E‑commerce in the manufacturing sector enables businesses to streamline operations, make smarter decisions, and scale effortlessly.
Cloud ERP Solution with Features Essential for E‑Commerce and D2C
- Manage Inventory from Your Online Stores in One App
- Set up Order Management Flow
- Manage Production Flow
- Analyze Profits
- Automate Business Routines to Enhance Productivity
Steps to Implement E‑Commerce for Manufacturing SMEs
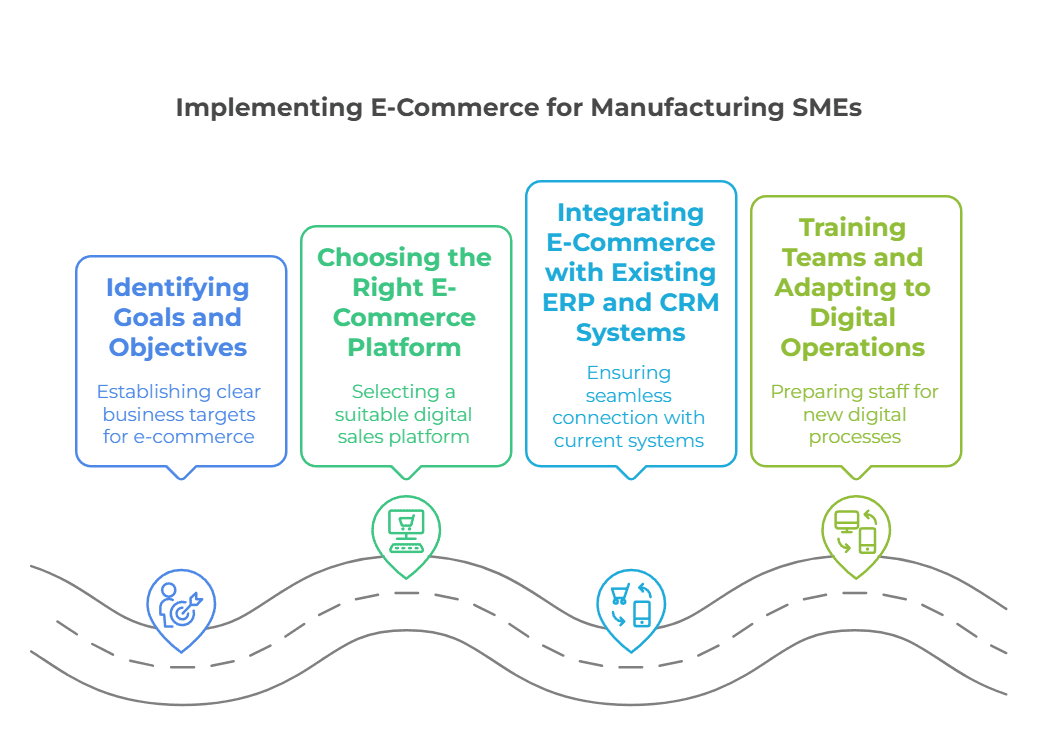
Successfully implementing e‑commerce for manufacturing companies involves several key steps. These steps ensure a smooth transition to digital operations and help meet business goals.
Identifying Goals and Objectives
Before starting, manufacturers must define what they want to achieve with e‑commerce applications in manufacturing.
- Goals could include increasing sales, improving efficiency, or expanding market reach.
- Clear objectives help guide the decision-making process and set benchmarks for success.
- Manufacturers should also consider how digital tools can solve specific pain points in their current processes.
Setting clear goals will help keep the focus on measurable outcomes and drive results.
Choosing the Right E‑Commerce Platform
Selecting the right platform is critical. The e‑commerce manufacturing platform should fit the needs of the business.
- Manufacturers should assess scalability to ensure the platform grows with their business.
- Integration with existing systems, such as ERP and CRM, is important to streamline operations.
- Cost is another factor to consider, as it should align with the company’s budget while offering sufficient features.
The right platform can make or break the e‑commerce experience, so thorough research is necessary.
Integrating E‑Commerce with Existing ERP and CRM Systems
To achieve seamless operations, e‑commerce manufacturers must integrate new e‑commerce platforms with existing systems like ERP and CRM.
- Syncing sales, inventory, and customer data across platforms improves accuracy and efficiency.
- Integration helps automate business processes in manufacturing and reduces manual work.
- A unified system also provides better visibility into business performance.
This integration enables smooth workflows and minimizes operational disruptions.
Training Teams and Adapting to Digital Operations
Training employees is vital to adapting to new digital tools.
- Teams must learn how to use the e‑commerce platform and handle customer interactions efficiently.
- Understanding the full e‑commerce in manufacturing industry process ensures a smooth operation.
- Regular training and updates help employees stay confident in using the platform.
A well-trained team will maximize the benefits of e‑commerce applications in manufacturing and drive success.
These steps lay a strong foundation for implementing e‑commerce for manufacturing businesses, leading to improved sales, operations, and customer relationships.
Challenges and Opportunities of E‑Commerce in Manufacturing
Adopting e‑commerce for manufacturing businesses presents both challenges and opportunities. Understanding these can help manufacturers navigate the shift towards digital operations effectively.
Common Challenges Faced by Manufacturers
Manufacturers often face several obstacles when implementing e‑commerce applications in manufacturing.
- Resistance to Change: Many employees and management are used to traditional ways of working. Adopting new e‑commerce tools may be met with reluctance.
- Technological Barriers: Small and medium-sized manufacturers may lack the infrastructure to support an advanced e‑commerce manufacturing system. Outdated hardware or software could hinder integration with existing processes.
- Initial Costs: Setting up an e‑commerce for manufacturing companies platform often requires a significant investment. The initial costs can be a concern for small businesses with limited budgets.
Despite these challenges, careful planning and gradual adoption can help ease the transition to e‑commerce.
Opportunities for Growth and Market Expansion
The e‑commerce in manufacturing industry offers significant growth potential.
- Access to New Markets: By moving online, manufacturers can reach a global customer base. B2B e‑commerce for manufacturers opens up opportunities to sell products to businesses worldwide.
- Competing with Larger Enterprises: Small and medium manufacturers can now compete with larger companies on a more level playing field. A well-implemented e‑commerce application in manufacturing can help SMEs gain visibility and attract more customers.
- Improved Customer Engagement: E‑commerce platforms allow manufacturers to offer better customer service. Real-time updates, streamlined ordering processes, and easy communication channels enhance the overall customer experience.
The digital shift allows manufacturers to explore new sales channels and grow their business by reaching customers they might not have accessed before.
Frequently Asked Questions on E‑Commerce in Manufacturing
E‑commerce is transforming how manufacturers operate. Here are answers to some of the most common questions about e‑commerce in the manufacturing industry.
What is the primary purpose of e‑commerce in manufacturing?
The main goal of e‑commerce for manufacturing businesses is to streamline operations. It helps automate business processes in manufacturing, making it easier to manage orders, inventory, and customer interactions. By shifting to an online platform, manufacturers can reach more customers and improve efficiency, reducing costs and manual work.
How is manufacturing e‑commerce different from retail e‑commerce?
Manufacturing e‑commerce primarily focuses on business-to-business (B2B) transactions. It deals with bulk orders and long-term relationships, unlike retail e‑commerce, which targets individual customers. This means manufacturers use e‑commerce to manage large-scale orders, wholesale pricing, and ongoing contracts.
Which e‑commerce platform is best for manufacturing SMEs?
The best e‑commerce platform for small and medium-sized manufacturers depends on their specific needs. B2B ecommerce for manufacturers often works well with platforms like Shopify, Magento, or even customized solutions. These platforms allow manufacturers to manage online stores, customer relationships, and inventory efficiently.
What are the key benefits of integrating e‑commerce with ERP systems?
Integrating e‑commerce manufacturing with ERP systems offers significant advantages. It enhances automation by linking business functions like sales, finance, and inventory. This ensures data accuracy and helps manufacturers manage resources and orders more efficiently. It also improves customer relationship management by providing a seamless experience.
Can small manufacturers afford e‑commerce solutions?
Yes, many platforms cater specifically to small businesses. These solutions are scalable and offer flexible pricing, allowing ecommerce manufacturers to grow at their own pace. With the right tools, even small manufacturers can benefit from ecommerce applications in manufacturing without a large initial investment.
What is the role of data analytics in manufacturing e‑commerce?
Data analytics helps manufacturers make informed decisions. By analyzing customer behavior, sales trends, and operational performance, manufacturers can improve processes and predict future needs. This is a key advantage of e‑commerce for manufacturing companies, as it supports data-driven strategies.
Is e‑commerce suitable for all types of manufacturing businesses?
Most manufacturing businesses can adapt to e‑commerce applications in the manufacturing sector. However, the success of e‑commerce for manufacturing companies depends on their specific needs. Some manufacturers may require more complex systems, while others may find simpler platforms sufficient.
How can manufacturers market their e‑commerce platforms effectively?
To drive traffic to their e‑commerce manufacturing sites, manufacturers can use strategies like search engine optimization (SEO), social media marketing, and partnerships. By building brand awareness and connecting with potential customers online, manufacturers can increase visibility and sales.
What are the major challenges in setting up e‑commerce for manufacturers?
Some of the challenges include integrating e‑commerce with existing systems, training employees, and overcoming resistance to change. Manufacturing e‑commerce requires investment in both time and resources to ensure smooth implementation.
What future trends are shaping e‑commerce in manufacturing?
The future of e‑commerce for manufacturing businesses includes advancements like AI-powered tools for better decision-making, augmented reality (AR) for product demonstrations, and blockchain for more transparent supply chains. These innovations promise to make e‑commerce in the manufacturing industry even more efficient and customer-friendly.


