In a fast-paced warehouse, orders, returns, and replenishments can accumulate within hours. Forklifts are in motion, pick lists keep printing, and teams work at full speed, yet the real slowdown often happens away from the shop floor. The disconnect between warehouse management and the rest of the business systems creates delays, mismatched data, and missed opportunities.
When warehouse operations run separately from the enterprise resource planning platform, inventory updates take hours to reach sales, purchase orders aren’t tied to live stock counts, and finance teams chase numbers that should already be in sync.
That gap is exactly what ERP was built to solve. And it isn’t just theory. Panorama Consulting’s 2024 ERP report shows that companies running ERP systems for a year or more consistently identify efficiency and inventory accuracy as the primary areas where the impact is felt.
An ERP warehouse management system closes these gaps by integrating warehouse tasks, sales, purchasing, and accounting into a single platform. Every receipt, transfer, and shipment update instantly reflects the entire business.
- What Is an ERP Warehouse Management System?
- ERP vs. WMS — Choosing the Right Fit for Your Warehouse
- Benefits of ERP with Warehouse Management
- Core ERP & WMS Features
- ERP & WMS Integration: How It Works
- ERP & WMS Use Cases
- How to Choose Between ERP and Standalone WMS
- Best ERP WMS Solutions (2026 List)
- Implementing ERP WMS Successfully
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions on ERP Warehouse Management
- List of Resources
What Is an ERP Warehouse Management System?
An ERP warehouse management system is a unified platform that combines the functions of an enterprise resource planning system with advanced warehouse management capabilities. Instead of running separate tools for accounting, inventory, order processing, and dispatch, an ERP WMS keeps all these processes connected in real-time.
Think about this in terms of day-to-day operations:
When I need to understand how ERP and Warehouse management work together,
I want a clear definition that shows exactly where it fits in my processes,
So, I can decide if it’s the right approach for my business.
✅ Solution: Kladana delivers ERP and warehouse functions in a single, real-time system, so every process is connected end-to-end
This integration turns the warehouse from an isolated function into a fully connected part of the business operation.
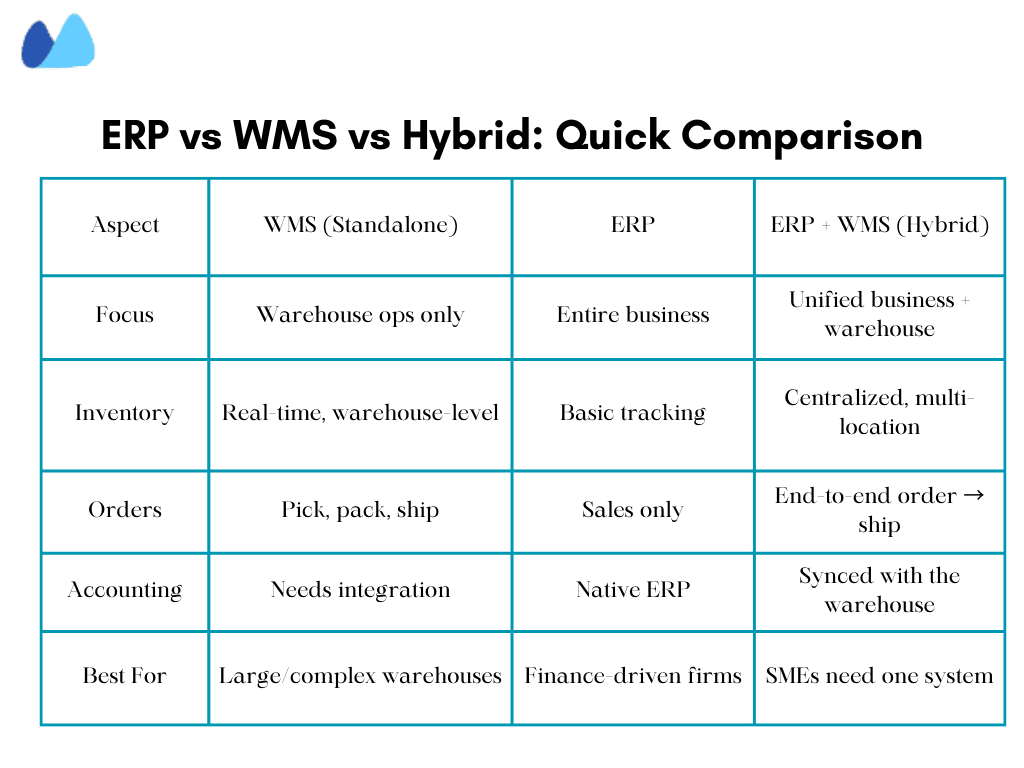
ERP vs. WMS — Choosing the Right Fit for Your Warehouse
An ERP manages company-wide processes, including accounting, procurement, and sales. While WMS focuses exclusively on warehouse operations like receiving, picking, packing, warehouse-only solution or a system that connects every department.
Standalone WMS vs. ERP — Integrated WMS
A standalone WMS offers deep warehouse functionality but operates independently of finance, purchasing, and sales systems. It always requires manual updates or integrations. An ERP-Integrated WMS delivers warehouse features within the same platform that runs the rest of your business, keeping data consistent and eliminating delays.
You can check and understand the table below if you want a transformation with ERP.
| ❌ Without ERP & WMS | ✅ With ERP & WMS |
| Manually logging warehouse stock in spreadsheets | Real-time stock sync in the ERP dashboard |
| Slow pick-pack processes with paper slips | Automate workflows with barcode scanning and optimized pick routes |
| Disconnected warehouse and accounting | Fully integrated ERP linking warehouse, sales, purchasing, and finance |
| Stock discrepancies are found only during audits | Instant discrepancy alerts triggered by live inventory tracking |
| Separate systems for returns are causing delays | Unified return management that updates stock and financial recording instantly |
| Time-consuming report preparation | On-demand, system-generated performance and inventory reports |
Benefits of ERP with Warehouse Management
Integrating warehouse management into your enterprise resource planning platform creates a connected workflow where inventory, orders, and finances are always in sync. This delivers three core benefits that have the most significant operational impact:
1. Real-Time Inventory Visibility
An ERP warehouse management system helps update the software instantly. This means you can check exact quantities in any warehouse at any moment, preventing overselling and enabling faster, more confident purchasing decisions.
2. Integrated Order-to-Fulfillment Workflows
Once a sales order is entered, the ERP WMS automatically generates pick lists, assigns tasks to warehouse staff, and updates the order status in real-time.
This eliminates manual coordination between departments, ensuring that customers receive their orders more quickly.
3. Accounting & Warehouse Sync
Every movement of stock is linked directly to your accounting records. Goods receipts, dispatches, and returns update financial data automatically, eliminating the need for manual entry and reducing errors, ensuring that your books always match your physical inventory.
🚛 Streamlined Fulfillment
- When I handle hundreds of orders daily,
- I want to automate picking and packing
- So I can ship faster and reduce human error
📈 Kladana ERP WMS connects orders to optimize pick lists automatically
Core ERP & WMS Features
An ERP warehouse management system combines essential warehouse functions with the power of enterprise resource planning. These are the core features that streamline operations and improve accuracy across every location:
1. Picking & Packing Automation
The system generates optimized pick lists, assigns tasks to staff, and updates order status automatically. This shortens fulfillment time and ensures orders are packed correctly the first time.
2. Barcode/RFID Integration
Scanners linked directly to the ERP validate every pick, pack, and dispatch in real-time. This reduces mis-picks, speeds up processing, and keeps inventory data accurate without manual entry.
3. Multi-Warehouse Management
Manage stock levels, transfers, and replenishments across all locations from a single dashboard. This makes it easy to balance inventory and avoid both overstock and shortages.
💡 Recommended Read: Multi-warehouse control is stronger when stock is organized inside each site. See our guide on warehouse bin storage to understand how bin systems cut picking time errors.
4. Reporting & Analytics
Get instant access to warehouse KPIs, order cycle times, and stock turnover rates. Use this data to spot inefficiencies, plan purchasing, and track performance over time.
🔗 ERP Warehouse Management for Faster, Error-Free Receiving
📦 When I receive large inbound shipments,
🔍 I want to scan barcodes directly into ERP,
⚡ So I can eliminate manual entry errors and speed up receiving
💻 In Kladana: Integrated barcode scanning updates ERP stock instantly
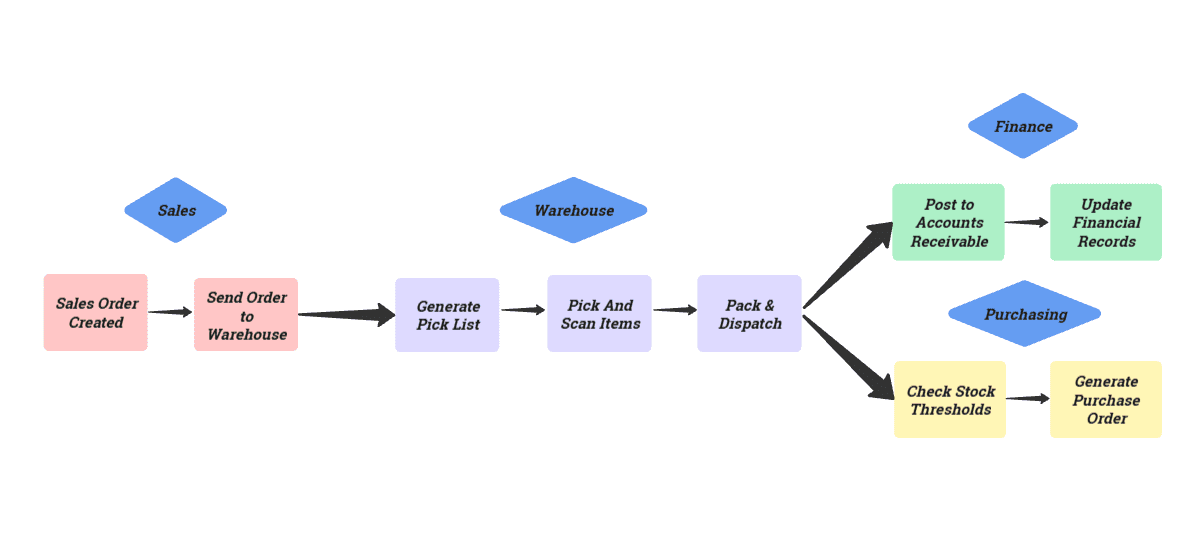
ERP & WMS Integration: How It Works
In an ERP warehouse management system, your warehouse module isn’t a separate tool. It’s built right into your ERP. That means every action in your warehouse automatically updates sales, finance, and purchasing in real-time, without requiring manual re-entry or waiting for a sync.
Here’s how the workflow plays out:
1. Sales Order Creation
You create a sales order in your ERP, and the system instantly generates a pick list in the warehouse module.
2. Picking & Packing
Your team scans each item as they pick, with inventory updating in real time so stock counts are always accurate.
📖 Recommended Read: Scanning during picking is what keeps ERP stock counts reliable. Read our guide on Barcoding in warehouse management to see how it reduces mis-picks and speeds up fulfillment
3. Goods Dispatch
Once packed, the order status changes to “shipped.” Shipping labels are created, and stock levels are adjusted instantly.
4. Accounting Updates
The dispatch automatically posts to your accounts receivable, so your books match your physical movements.
5. Purchasing Triggers
If the stock drops below your set threshold, the ERP automatically raises a purchase order without requiring manual intervention.
ERP & WMS Use Cases
An ERP warehouse management system isn’t limited to one type of business model. It adapts to different industries and operational scales. Here’s how it works in practice.
1. SMEs Scaling Logistics
If your small or mid-sized business is growing rapidly, you need a system that keeps operations running smoothly as order volumes increase. An ERP & WMS gives you centralized inventory control, automated workflows, and integrated financial updates.
2. Manufacturers Managing Raw Materials & Finished Goods
In manufacturing, tracking both raw material and finished products is critical. An ERP & WMS connects production schedules, stock movements, and procurement so you always know what’s on hand and what’s needed next.
3. 3PL & Distribution Companies
For third-party logistics providers, the challenge is managing multiple clients’ stock without mix-ups. An ERP WMS assigns inventory ownership, automates order processing, and provides live reporting for each client.
These examples illustrate how ERP WMS can be tailored to various industries. And it’s not just isolated success stories. According to Grand View Research, the Global WMS market is projected to grow from $2.88 billion in 2024 to $8.38 billion by 2030.
How to Choose Between ERP and Standalone WMS
Choosing between a standalone warehouse management system and an ERP with integrated WMS comes down to your operational needs, budget, and long-term plans. You’ll want to consider how much integration you need with other business processes, and how much warehouse-specific depth you require.
Key comparison:
| Factor | Standalone WMS | ERP-Integrated |
| Scope | Focused only on warehouse functioning such as receiving, picking, packing, shipping, | Covers warehouse plus finance, sales, purchasing, and reporting |
| Data Sync | Requires integration to share data with other systems | Single database with real-time updates across all modules |
| Implementation Cost | Lower upfront cost, but integration expenses may add up | Higher upfront cost, but no ongoing integration expenses |
| Scalability | Limited to warehouse operations | Scales with your business across multiple departments and locations |
| Reporting | Warehouse performance only | Company-wide KPIs and cross-departmental insights |
Best ERP WMS Solutions (2026 List)
If you’re evaluating an ERP warehouse management system, you’ll find options that range from SME-focused solutions to large-scale enterprise platforms. The right choice depends on your industry, operational complexity, and growth plans.
1. Kladana
It is built specially for SMEs in manufacturing, distribution, and e-commerce. Kladana combines ERP functions with warehouse management in a single, real-time platform.
You can manage stock across multiple warehouses, automate picking and packing. It syncs financials instantly and tracks KPIs from a single dashboard, eliminating complexity and the high costs associated with enterprise-level systems.
2. NetSuite
It is best suited for mid-to-large enterprises. NetSuite offers robust warehouse features, such as wave picking, customization, and mobile scanning. It also features powerful ERP modules for finance, CRM, and supply chain management.
3. SAP Business One
It is specially designed for manufacturing and distribution businesses. They offer built-in warehouse tools for batch tracking, serial number management, and managing multi-location stock.
4. Odoo
It is an open-source ERP platform with a modular WMS app. It is flexible, cost-effective, and can be tailored to niche processes. They are ideal if you have strong in-house technical resources.
Implementing ERP WMS Successfully
Rolling out an ERP warehouse management system takes planning, but with the right approach, you can avoid disruption and get faster ROI. Follow these steps to ensure a smooth transition.
1. Planning & Data Migration
Before you start, map your current warehouse processes and decide which workflows you’ll keep, optimize, or replace.
Clean and standardize your existing data, product codes, supplier details, and customer info. So the migration doesn’t carry over errors. Create a phased rollout plan that prioritizes your highest impact functions first.
2. Integrating with ERP/Warehouse
If you already use an ERP without a warehouse module, integration will connect your stock movements to finance, purchasing, and sales.
Set up barcode scanners, label printers, and mobile devices so your team can work in real time. Test the integration on a small batch of orders before deploying it across the entire warehouse.
3. Testing & Launch
While you are testing and launching, train staff on the new workflows and devices. Assist them with a quick-reference guide for everyday tasks. Once you go live, monitor KPIs such as order accuracy, picking time, and stock discrepancies to measure early wins.
Conclusion
An ERP warehouse management system isn’t just about keeping stock organized. It’s about connecting your warehouse to every part of your business.
- When your sales orders trigger, the picks are made instantly.
- Your accounting updates the moment goods ship
- Purchasing reacts before you hit a stockout
With the right ERP WMS, you can cut manual work, boost accuracy, and make faster, data-driven decisions. Begin by mapping your needs, planning a clean migration, and selecting a platform that aligns with your scale and goals. The sooner you integrate your warehouse into your ERP, the sooner you turn it from a cost center into a growth driver
🚀 End double data entry — integrate ERP & WMS in Kladana
Make picking, packing, and payments flow seamlessly in one system
Frequently Asked Questions on ERP Warehouse Management
Which ERP products will help streamline my warehouse operations and shipping processes?
You’ll achieve the most impact from ERP systems with native WMS capabilities, such as wave picking, carrier integration, barcode scanning, and returns management. Shortlist ERPs that connect sales, warehouse, shipping, and accounting in real time and support your carriers and marketplaces out of the box.
What is the difference between ERP and WMS?
A WMS optimizes warehouse tasks, including receiving, picking, packing, and shipping. An ERP manages company-wide functions. An ERP warehouse management system combines both. So that data stays consistent across departments.
Is warehousing a function of ERP?
Yes. Many ERPs include a warehouse management module, which encompasses functions such as location management, transfers, cycle counts, put-away, and pick/pack/ship. Depth varies by vendor. If you require advanced features, opt for an ERP with a robust WMS rather than a basic inventory add-on.
What is an ERP system in a warehouse?
It’s a setup where your warehouse operations run inside the ERP, so every scan, pick, dispatch, and return instantly updates inventory, orders, and accounting.
How do I optimize my warehouse operations with ERP?
Standardize locations & SKUs, enable barcode/RFID. Use optimized pick lists (batch/zone/wave). Automate your reorder points and track KPIs. Try to keep everything inside one ERP WMS so that changes are updated everywhere.
Can an ERP WMS handle multiple warehouses and multi-location shipping?
Yes. You can manage stock by warehouse, bin, and IoT/serial. Always try to automate inter-warehouse transfers and route orders to the closest shipping location to cut transit time and cost.
Does an ERP WMS support barcode/RFID and true real-time inventory?
Yes. It scans at receiving, picking, packing, and dispatch to update inventory in real time and validates the correct item/location. It reduces mis-picks and cycle count variances.
What’s the typical implementation timeline for an ERP WMS, and how do I reduce risk?
SME rollouts often take weeks to a few months, depending on data cleanup, device setup, and integrations. You reduce risk by phasing, pilot one area, run parallel counts, train users, and monitor go-live KPIs.
How do costs compare between standalone WMS and ERP with WMS?
A standalone WMS can be cheaper upfront, but it requires integrations, time, and ongoing maintenance. An ERP with WMS may cost more initially, but it avoids sync overhead and gives unified reporting, often lowering the total cost of ownership as you scale.
What are the must-have features in an ERP warehouse management system?
You can look for:
- Picking & packing automation
- Barcode/RFID
- Multi-warehouse control
- Return Merchandise Authorization
- Cycle counts
- IoT/serial tracking
- Shipping integrations/labels
- Reporting & analytics
List of Resources
- Panorama Consulting Group: The 2024 ERP report
- Grandview Research: Warehouse Management System Market Summary
Read‑alikes
Warehouse Inventory Management: a Complete Guide to Tools, Tips, and Systems for 2026
Warehouse Management System Process Flow: Steps, Charts, and SOP Templates
How Does a Pick and Pack Warehouse Work in 2026 — What Improves Its Efficiency?
Warehouse Inventory Management: a Complete Guide to Tools, Tips, and Systems for 2026



