Stock errors cost money. A missed reorder alert, a wrong item sent to a customer, or expired raw materials in storage — all of these can hurt a business. That’s where ERP inventory management makes a difference.
It helps SMBs in India keep stock under control, avoid costly mistakes, and plan better. The system connects purchases, warehouses, sales, and even production — all in one place. No need to update multiple spreadsheets or guess what’s in stock.
With the right ERP inventory management software, you can run lean, reduce waste, and grow faster — even with a small team.
According to the research made by International Journal of Research in Engineering and Science, ERP inventory management is crucially valuable to business owners.
This web application includes logical tools for determining ideal inventory levels and automatically identifying appropriate replenishment tactics. It also contains features that allow it to detect stock levels, calculate reorder points automatically, and alert users to imminent stock-outs.
In this article we will look at how ERP systems work and how to choose the right one for your business.
- What Is ERP Inventory Management?
- Key Functions of ERP Inventory Modules
- Benefits of ERP for Inventory and Material Management
- How ERP Inventory Management Works (Step-by-Step)
- Who Needs ERP Inventory Management Software?
- Choosing ERP Inventory Management System
- ERP Inventory Management with Kladana
- Conclusion: Why Indian SMEs Should Choose ERP Inventory Tools
- Frequently Asked Questions about ERP Inventory and Material Management
- List of Resources
What Is ERP Inventory Management?
ERP inventory management means using ERP software to handle everything related to stock. For example, you can keep track of items or plan what to buy next. It gives one view of all inventory data across locations. This helps avoid confusion, mistakes, and extra costs.
Traditional inventory systems often work alone. But ERP inventory management software connects inventory with sales, purchasing, production, invoicing, reporting, etc. It updates stock levels automatically when a purchase is received, when a product is sold, or when raw materials are used. This saves time and reduces errors from manual work.
Inventory Module Inside ERP
The ERP inventory module is one part of the ERP system. It records all item movements — incoming, outgoing, and transfers. The module also helps set reorder levels, manage safety stock, and generate real-time inventory reports. For Indian businesses, some ERP systems also support local units of measurement and tax rules.
💡 What makes ERP different is that the inventory module talks to other modules. For example:
- When a sales order is created, the inventory is reserved.
- When a purchase order is received, the stock is updated.
- When production starts, raw materials are deducted from stock.
This connection means less manual work and fewer errors.
Inventory vs. Material Management
ERP in material management goes deeper than basic inventory control. It tracks raw materials, components, and finished goods. It helps manage storage, wastage, shelf life, and quality.
This is useful for manufacturers who need to handle materials at different production stages. While inventory focuses on stock quantity, material management focuses on the full cycle — from purchase to use to finished product.
🧊 4 Free Inventory Ckecklists
Learn how to manage stock, set up your warehouse, track barcodes, and build product cards for e‑commerce — even if you’ve never done it before
✅ Inventory management
✅ Warehouse setup
✅ Barcode tracking
✅ E-commerce product cards
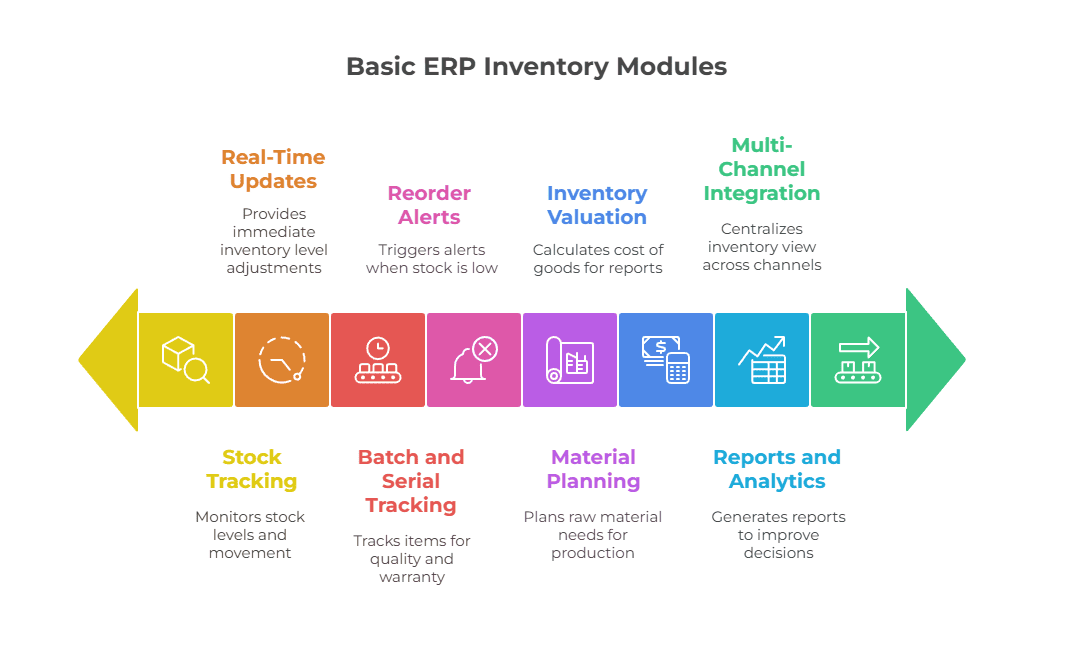
Key Functions of ERP Inventory Modules
An ERP inventory module helps manage stock in a smart and organised way. It connects inventory records with purchase, sales, and production data. Below are its main features that support daily operations.
Stock Tracking
ERP for inventory management tracks every item from the moment it enters your business to the moment it leaves. It shows where stock is stored, how much is available, and when it was last moved. This helps reduce theft, loss, and stock mismatches.
Real-Time Updates
Stock levels change all the time. Real-time tracking ensures that any sale, return, or purchase updates the system immediately. This means your team always sees the correct data, without waiting for manual reports.
Material Planning
For manufacturers, ERP in material management helps plan how many raw materials are needed. It checks what is in stock and calculates what needs to be ordered for production. This avoids delays and keeps the workflow smooth.
Reorder Alerts
You can set minimum stock levels for each item. Once inventory drops below that point, the system sends an alert. This helps avoid stockouts and ensures that popular items are always available for sale or production.
Batch and Serial Tracking
Some products need batch numbers or serial numbers (like medicines, electronics, or food items). An ERP inventory management system can track these for quality control and warranty claims. You’ll know when each batch was made or where a faulty product came from.
Inventory Valuation Methods
Inventory value affects profits and taxes. ERP systems support methods like FIFO (First In, First Out), LIFO (Last In, First Out), and Weighted Average. This helps calculate the cost of goods sold and prepare accurate reports.
Reports and Analytics
ERP systems generate detailed reports and analytics on inventory levels, stock movements, and other key metrics. This helps businesses identify trends, forecast demand, and improve decision-making.
Multi-Channel Integration
ERP systems can integrate with various sales channels, such as e-commerce platforms and retail stores, providing a centralized view of inventory and sales data.
Benefits of ERP for Inventory and Material Management
Using ERP for inventory management helps businesses get more control over their stock and materials. Let’s explore the main advantages of ERP inventory management.
Centralized Data
With ERP inventory management software, all stock and material data is stored in one place. Everyone sees the same numbers — whether they are in the warehouse, accounts, or sales. This reduces miscommunication and speeds up decision-making.
✔️ For example, if a purchase manager places an order, the warehouse team can track when the stock arrives. At the same time, the finance team can see the payment status. No need for multiple spreadsheets or back-and-forth emails.
Protection from Stockouts and Overstocking
Stockouts can stop production or delay customer orders. Overstocking ties up money in unused items. An ERP inventory module helps strike the right balance. It alerts users before items run out and shows slow-moving stock that needs to be cleared.
✔️ This is useful for businesses with seasonal goods or fast-moving SKUs. It helps save space, avoid losses, and keep customers happy.
Accurate Forecasting
The system uses past data to forecast future needs. You can see what sells well, which items are returned often, and which raw materials are used the most. This helps plan purchases, production, and sales more accurately.
✔️ With better planning, you can avoid last-minute buying and reduce emergency costs.
Integration with Purchase, Sales, and Production
ERP inventory management connects inventory with other key functions. When a sales order is placed, the system checks available stock. When goods are received, purchase and inventory records update together. This full integration helps reduce double work and errors.
✔️ You don’t need to enter the same data in different systems. Everything is linked — saving time and ensuring accuracy.
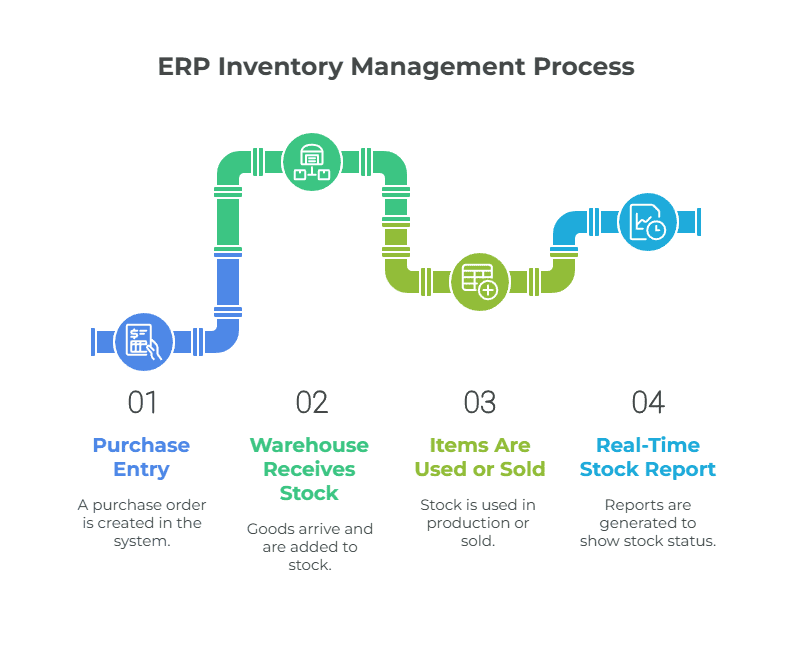
How ERP Inventory Management Works (Step-by-Step)
ERP inventory management connects all steps of the inventory process. Each action updates the system, so everyone sees real-time stock levels. Here’s how it works in a typical business:
Step 1 — Purchase Entry
The process starts when a purchase order is created in the system. This can be for raw materials, packaging, or finished goods. The system records the order details and links it to the supplier.
Step 2 — Warehouse Receives Stock
When the goods arrive, the warehouse team checks the delivery and updates the ERP system. The ERP inventory module then adds the items to available stock. If there are any differences between ordered and received quantities, the system flags them.
Step 3 — Items Are Used or Sold
Once stock is in the system, it can be used in production or sold to customers. The ERP automatically adjusts inventory levels when a sales invoice is created or when raw materials are issued for production. This avoids mistakes and shows accurate stock balance.
Step 4 — Real-Time Stock Report
The system keeps track of all movements — purchases, issues, transfers, and sales. You can generate real-time reports showing stock quantity, value, expiry, or location. This helps business owners make decisions based on up-to-date data.
🫸 Stop guessing what’s in stock 🫷
Upgrade from spreadsheets to Kladana’s ERP Inventory module — track, monitor, and optimize inventory effortlessly
Who Needs ERP Inventory Management Software?
ERP inventory management software is not just for large companies. It helps many types of businesses that want to work faster, avoid stock mistakes, and grow with less stress.
SMEs with Complex Supply Chains
Many small and medium enterprises deal with multiple suppliers, vendors, and delivery partners. Without the right tools, stock tracking becomes hard and errors happen.
⤴️ With ERP for inventory management, they can see everything in one place — what’s ordered, what’s received, and what’s still needed. This makes supply chain planning much easier.
Manufacturers
Manufacturers must handle raw materials, semi-finished items, and finished goods. Delays in material supply can stop production. Errors in stock can waste time and money.
⤴️ An ERP inventory module helps manufacturers manage inputs and outputs across all stages. It links with production, so material usage is tracked automatically.
Multi-Warehouse Businesses
When stock is stored in different locations, it’s easy to lose track. One warehouse might have too much of one item, while another is out of it.
⤴️ ERP inventory management shows stock levels across all warehouses. You can transfer items, check expiry dates, and avoid over-ordering. This is helpful for wholesalers, distributors, or regional offices.
D2C Companies
Direct-to-consumer brands manage sales on multiple platforms — online stores, marketplaces, or social media. Keeping inventory updated across all channels is hard without automation.
⤴️ ERP inventory management software syncs stock across systems and reduces overselling or stockouts. It also connects with shipping and returns, so customers stay satisfied.
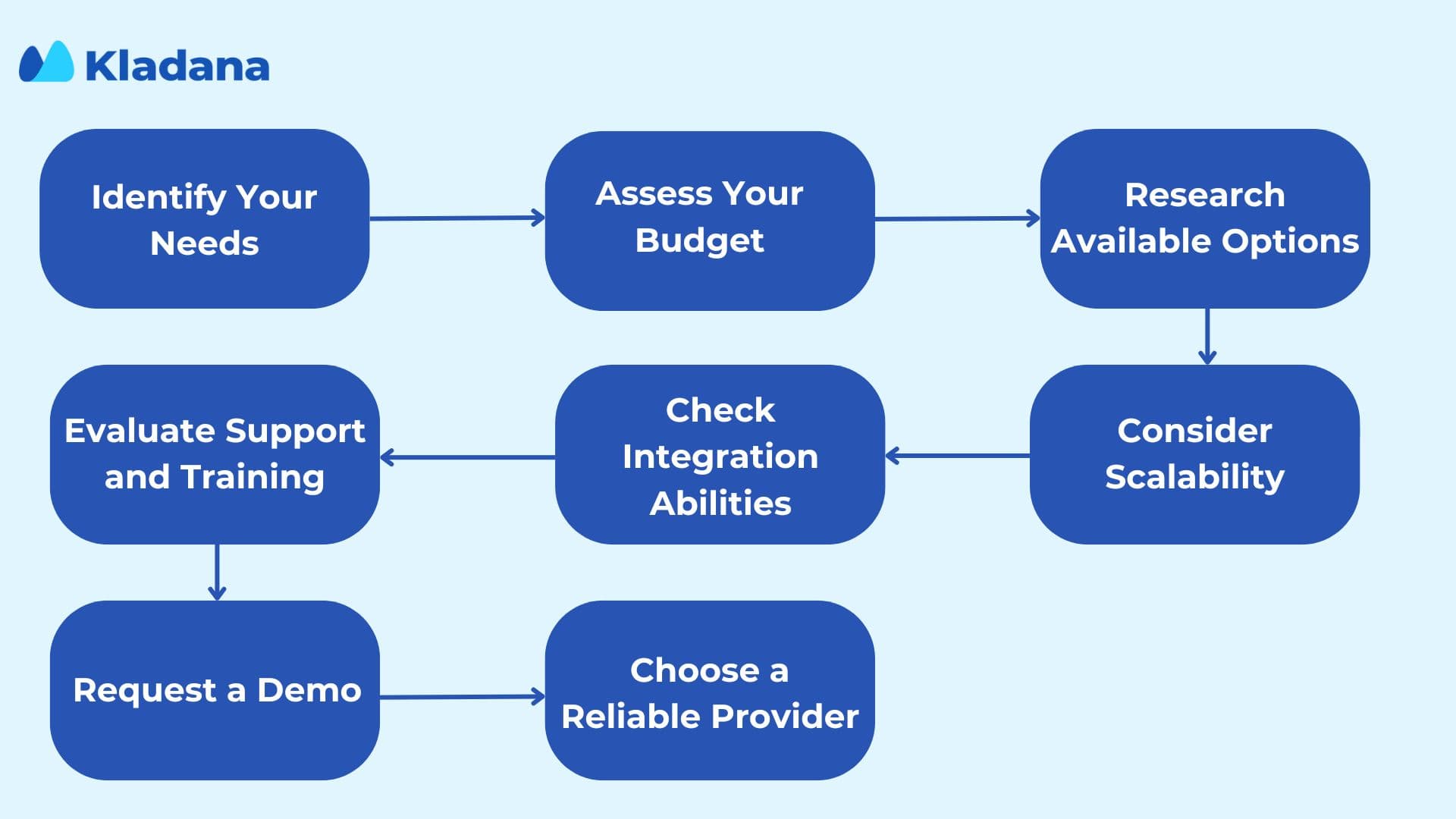
Choosing ERP Inventory Management System
Selecting the right ERP solution can be daunting. This step‑by‑step guide will help you navigate through the selection process, ensuring you make an informed decision that aligns with your business needs and goals.
Step 1. Identify Your Needs
Begin by understanding your business’s inventory management requirements. Determine the key features you need in an ERP system, such as inventory tracking, order management, and integration capabilities.

Step 2. Assess Your Budget
Evaluate your budget to ensure you can afford the ERP system. Consider not just the initial cost but also ongoing expenses like maintenance and upgrades.
Step 3. Research Available Options
Explore different ERP inventory management systems available in the market. Look for reviews, compare features, and consider the reputation of the providers.
Step 4. Consider Scalability
Choose an ERP system that can grow with your business. Ensure it can handle an increase in inventory volume and complexity as your business expands.

Step 5. Check Integration Abilities
Verify that the ERP system can integrate with your existing software, such as accounting or CRM systems, to streamline operations.

Step 6. Evaluate Support and Training
Look for a provider that offers comprehensive support and training to help your team make the most of the ERP system.
Step 7. Request a Demo
Before making a final decision, request a demo of the ERP system to see how it works in action and ensure it meets your needs.
Step 8. Choose a Reliable Provider
Select a reputable ERP provider with a track record of successful implementations and ongoing support for their clients.
ERP Inventory Management with Kladana
Kladana offers ERP inventory management software tailored to small and medium businesses. It helps control stock, plan purchases, and run production — all from one platform.
Localized Features for Indian Businesses
Kladana supports Indian tax rules like GST. You can set the right tax regime for your company and each counterparty, add the State and GSTIN, and include HSN or SAC codes in your product and service cards. GST (CGST + SGST or IGST) is automatically applied to all sales and purchase transactions.
You can also set Indian units of measurement such as litres, kilograms, or metres. These features make it easier to stay compliant and reduce manual errors.
Cloud-Based and Mobile Friendly
Kladana is a cloud-based system. You don’t need to install anything — just log in from your browser. It works on laptops, tablets, and phones. This means you can check stock levels or approve orders from anywhere.
For busy owners and managers, having access on mobile browser helps avoid delays and keeps work moving.
Affordable for Growing Businesses
Many Indian SMEs hesitate to buy ERP systems because they think it’s too costly. Kladana offers flexible plans that start from $60 only and grow with your business.
You only pay for what you use. This makes ERP for inventory management affordable even for new or small teams.
Integration of Inventory, Purchase, and Production
Kladana connects stock records with purchases and manufacturing. When you order raw materials, stock updates automatically. When production starts, the system deducts materials and adds finished goods. This avoids manual updates and keeps stock data accurate.
With one system handling inventory, procurement, and production, your team works faster and makes fewer mistakes.
Choose Kladana to automate your inventory management.
Without Kladana — Excel & notebooks
There is no clear picture of the inventory.
- An entrepreneur isn’t aware of products on hand, reserved, or in transit, their exact locations, expiry dates, etc.
- When one suddenly runs out of an item, they lose profit while waiting for new supplies
With Kladana
You see the whole picture of stock. No guesswork in inventory management.
- Get notifications if new supplies are needed
- Write off expired products in time
- Monitor stock movement
Subscribe for a demo and learn how to manage your inventory more efficiently.
Conclusion: Why Indian SMEs Should Choose ERP Inventory Tools
- Managing stock with spreadsheets or paper often leads to errors, delays, and lost sales. ERP inventory management helps fix that. It connects inventory to sales, purchase, and production — so your data is always accurate, and your team works faster.
- Indian businesses benefit even more from ERP inventory management software that understands local needs — GST, regional units, and mobile access. With better control, you avoid stockouts, overstocking, and last-minute buying.
📋 Want to see how it works in real life?
🔊 Try Kladana. No card needed for a 14-day free trial.
Frequently Asked Questions about ERP Inventory and Material Management
Below are answers to common questions about ERP inventory management and material handling.
What is ERP inventory management?
ERP inventory management is a system that helps businesses track and manage their inventory in real-time. It integrates various processes such as purchasing, warehousing, and sales to provide a comprehensive view of inventory levels and movements.
What is the difference between inventory and material management?
Inventory management focuses on stock levels; material management includes procurement, storage, usage, and movement.
Can ERP inventory management integrate with other systems?
Yes, ERP inventory management systems are designed to integrate with other business systems, such as accounting software, CRM systems, and e-commerce platforms. This integration enables seamless data flow and eliminates manual data entry errors.
Is ERP inventory management suitable for small businesses?
Yes, ERP inventory management can be beneficial for small businesses as well. While the initial implementation may require some investment and resources, the long-term benefits, such as improved efficiency and cost savings, outweigh the initial costs.
How does ERP inventory management help in reducing costs?
ERP inventory management helps in reducing costs by optimizing inventory levels, minimizing stockouts, and eliminating excess inventory. It also streamlines processes, reduces manual errors, and improves overall operational efficiency.
Can ERP inventory management help in forecasting demand?
Yes, ERP inventory management systems often include features for demand forecasting based on historical data, trends, and seasonality. This helps businesses anticipate future demand and plan their inventory accordingly.
What are the best ERP inventory modules?
Key features to look for include real-time inventory tracking, demand forecasting, order management, warehouse management, and integration capabilities. Additionally, scalability, user-friendliness, and support are important considerations.
How can businesses ensure a successful implementation of ERP inventory management?
To ensure a successful implementation, businesses should first conduct a thorough analysis of their current inventory management processes and requirements. They should also choose a reliable ERP vendor, provide adequate training to employees, and regularly monitor and evaluate the system’s performance.
What are some common challenges faced during ERP inventory management implementation?
Common challenges include resistance from employees, data migration issues, lack of proper training, and integration complexities. However, these challenges can be overcome with proper planning, communication, and support from top management.
Can ERP software track inventory in real time?
Yes. Modern ERP systems offer real-time updates on stock movements and availability.



