As businesses grow, managing operations and customer relationships becomes increasingly complex. Two powerful solutions — ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) and CRM (Customer Relationship Management) — offer the tools to streamline processes and improve business efficiency. ERP centralizes core operations like inventory management, finance, and production into one system, ensuring smoother workflows. On the other hand, CRM focuses on enhancing customer interactions, helping teams manage leads, track sales, and improve service quality.
However, businesses often overlook the subtle, yet significant, overlap between ERP and CRM. Both systems contribute to business growth but serve different needs. For small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) looking to automate their workflows, understanding which system to adopt, or whether integrating both would be more beneficial, can be the key to unlocking efficiency. Choosing the right solution could save your business both time and money, while future-proofing your operations.
Understanding ERP and CRM Systems
For small and medium-sized businesses, understanding the differences between ERP and CRM systems is essential to streamline operations and improve customer relationships. Both systems offer distinct advantages, but their focus and implementation vary significantly.
What is ERP? (Enterprise Resource Planning)
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems are designed to integrate and automate core business functions such as finance, inventory management, procurement, and production. For small and medium-sized businesses, an ERP acts as a central hub that connects various departments, allowing for real-time data access and improved decision-making. A well-implemented ERP can reduce manual errors, optimize workflows, and improve resource allocation.
Key advantages of ERP systems include:
- Centralized data for streamlined operations
- Real-time reporting across departments
- Automation of repetitive tasks, reducing operational costs
- Scalability to grow with your business
What is CRM? (Customer Relationship Management)
While ERP focuses on operational efficiency, CRM systems are dedicated to managing customer relationships and enhancing front-end processes. CRM (Customer Relationship Management) systems, by contrast, focus on optimizing customer-facing functions. These tools are invaluable for managing interactions across sales, marketing, and customer service. CRM systems help businesses build better relationships by tracking customer interactions, improving lead management, and providing actionable insights into customer behavior.
Key benefits of CRM systems:
- Improved customer retention through better service
- Sales pipeline management for higher conversion rates
- Automated communication to nurture leads efficiently
- Enhanced customer insights for personalized experiences
Both ERP and CRM systems are essential for business growth, but they focus on different areas of management, which makes choosing the right system critical.
Without Kladana — Excel & Paper Records
The inventory status remains unclear: Business owners lack insight into available stock, reserved items, products in transit, their exact storage locations, and expiration dates. There’s a risk of stockouts, resulting in lost revenue while awaiting restocks.
With Kladana
You gain full visibility over inventory, removing any uncertainty: Receive timely alerts for replenishments. Promptly discard expired products. Easily track stock movements.
Key Differences Between ERP and CRM
While both ERP and CRM systems help businesses optimize operations, they serve distinct purposes. ERP is centered on internal processes, such as resource management and inventory control, while CRM focuses on external processes like customer interactions and sales. Understanding their key differences can guide small and medium-sized businesses in choosing the right solution to streamline their workflows.
| Aspect | ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) | CRM (Customer Relationship Management) |
Primary Focus |
Optimizing and automating internal operations (inventory, finance) |
Managing customer relationships and improving sales |
Key Functions |
Procurement, production, inventory, accounting |
Sales tracking, customer service, marketing automation |
User Base |
Operations, finance, and supply chain teams |
Sales, marketing, and customer service teams |
Data Centralization |
Centralizes business operations for better resource management |
Centralizes customer data for improved relationship building |
Impact on Business |
Increases operational efficiency and reduces costs |
Enhances customer satisfaction and boosts sales growth |
Scalability |
Designed to scale with complex business processes |
Focused on growing customer engagement and retention |
The main takeaway is that ERP integrates and automates business operations, while CRM enhances customer-facing activities. When implemented together, ERP and CRM offer a complete solution that addresses both operational efficiency and customer relationship management, creating a seamless business environment for long-term growth.
The Benefits of ERP and CRM Systems
Both ERP and CRM systems offer substantial benefits to small and medium-sized businesses, driving improvements in business automation, operational efficiency, and growth. While ERP focuses on automating internal processes, CRM enhances customer interactions and sales management. Together, they provide a comprehensive toolkit that can significantly boost business performance.
Benefits of ERP for Business Automation
ERP systems are vital for automating multiple business functions, from inventory management to financial tracking. By centralizing data from various departments, ERP allows businesses to streamline workflows and reduce manual tasks. For instance, instead of relying on separate software for inventory control, accounting, and production, an ERP system integrates all these functions into one cohesive platform.
- Inventory Management: Real-time data ensures stock levels are optimal, reducing the risk of overstocking or stockouts.
- Financial Accuracy: Automating accounting processes reduces errors, ensuring accurate financial reporting.
- Production Efficiency: By automating supply chain processes, ERP enhances production planning and resource allocation.
Benefits of CRM for Sales and Customer Management
CRM systems enhance sales and customer relationship management by centralizing customer data and automating key processes such as lead tracking and communication. This not only improves the efficiency of sales teams but also fosters better customer engagement and retention.
- Sales Optimization: CRM tools help prioritize leads, ensuring that sales teams focus on high-potential customers.
- Customer Engagement: Automated follow-ups and personalized communication nurture customer relationships.
- Data-Driven Insights: With detailed customer data, businesses can offer personalized experiences, boosting satisfaction and retention.
How Both Systems Improve Decision-Making
Both ERP and CRM systems offer real-time data, empowering business leaders to make informed decisions. ERP systems provide insights into operational efficiency, inventory levels, and financial performance, while CRM systems offer deep visibility into customer behaviors, sales trends, and service metrics.
With centralized data from both systems, decision-makers can:
- Identify inefficiencies in production, supply chain, or customer service.
- Anticipate customer needs and optimize marketing strategies.
- Forecast future demand based on sales and operational trends.
By leveraging the combined insights from ERP and CRM, businesses can respond faster to market changes, improve strategic planning, and boost overall growth.
Read‑alikes
ERP Inventory Management: 12 Benefits for Your Business in Full Guide
Top 20 ERP Software for SMEs in India and Across the World 2025
MRP vs ERP: A Comprehensive Guide to Business Management Solutions
ERP and CRM Integration: The Best of Both Worlds
Integrating ERP and CRM systems creates a unified solution for businesses, combining the operational efficiency of ERP with the customer-centric capabilities of CRM. This integration enables seamless data flow across departments, eliminating redundancies and enhancing business processes from production to customer engagement.
How ERP and CRM Integration Works
ERP and CRM integration involves connecting both systems to share real-time data. This is typically achieved through APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) or third-party integration tools. The shared data enables departments to access the same up-to-date information, ensuring a smooth workflow between operations and customer management.
For example, when a sales order is placed through the CRM, the ERP system automatically updates inventory levels, triggers production schedules, and manages accounting. This eliminates the need for manual data entry and reduces the risk of errors.
Business Benefits of ERP and CRM Integration
By integrating ERP and CRM, businesses can break down data silos, streamline operations, and enhance customer experiences. Key benefits include:
- Improved Collaboration: Teams across departments access the same data, leading to better coordination between sales, production, and finance.
- Increased Efficiency: Automation of tasks such as order processing and inventory updates reduces manual work, saving time and reducing errors.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Real-time visibility into both operational and customer data allows businesses to respond faster to customer inquiries and issues.
Examples of ERP and CRM Integration in Action
A mid-sized manufacturing company, for example, may integrate ERP and CRM to manage sales orders and inventory in real-time. The sales team can instantly see stock availability and provide accurate delivery timelines to customers. Meanwhile, production teams receive automatic updates on new orders, ensuring timely fulfillment. This level of integration not only boosts efficiency but also elevates customer satisfaction, resulting in increased loyalty and repeat business.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Business
Deciding between ERP and CRM, or integrating both, depends on your business’s specific needs. Here’s how to determine which solution best fits your operational goals and challenges.
When to Choose ERP
Consider ERP if your business’s primary need is to streamline internal processes and manage complex operations efficiently.
- Focus on internal processes: ERP is ideal for businesses that need to streamline core operations such as inventory management, financial accounting, and production scheduling.
- Automation of complex tasks: If your business requires automation of daily tasks across departments, such as finance, supply chain, and procurement, ERP can centralize these functions.
- Suitable for growth: For companies facing rapid growth or expanding product lines, ERP provides the structure to maintain control over resources and workflows.
- Example: Manufacturing companies that need real-time tracking of raw materials, production timelines, and financial transactions benefit significantly from ERP systems.
When to Choose CRM
Opt for CRM if your business aims to enhance customer service, sales performance, and lead management.
- Customer-focused operations: CRM is the best fit for businesses that aim to enhance customer service, sales performance, and lead management.
- Optimizes customer interactions: If managing a growing customer base and improving communication are key priorities, CRM tools provide the necessary functionalities to engage clients and boost loyalty.
- Drives sales and marketing: For businesses looking to improve lead generation and sales funnel management, CRM helps by centralizing customer data and streamlining sales processes.
- Example: CRM systems are ideal for service-based businesses or sales-driven companies aiming to nurture customer relationships and improve retention.
When to Consider Both
For businesses requiring both operational efficiency and superior customer management, integrating ERP and CRM systems can be the best approach. Here’s how they complement each other:
| ERP | CRM |
Focuses on internal operations like inventory, finance, and production |
Focuses on external operations like sales, customer relations, and marketing |
Ideal for managing resources, streamlining workflows, and ensuring compliance |
Best for driving customer engagement, improving lead generation, and managing sales pipelines |
Centralizes data across departments for seamless coordination |
Optimizes customer interaction and boosts retention through streamlined communication |
Suitable for industries such as manufacturing, retail, and logistics |
Best for sales teams, service providers, and companies with strong customer relationships |
By combining both, businesses can achieve operational excellence and customer satisfaction, ensuring long-term growth and efficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions on ERP vs CRM
Addressing common queries about ERP and CRM systems helps clarify their functionalities, benefits, and how to choose the right solution for your business.
What is the main difference between ERP and CRM?
The primary distinction between ERP and CRM systems lies in their focus areas
- ERP: Concentrates on internal business operations, such as inventory management, financial accounting, and production processes.
- CRM: Specializes in managing customer relationships, enhancing sales performance, and optimizing customer service interactions.
Can ERP and CRM be integrated?
Yes, integrating ERP and CRM systems is highly beneficial. This integration allows businesses to synchronize customer data with internal processes, creating a cohesive view of operations and customer interactions. As a result, companies can improve efficiency, reduce data silos, and enhance decision-making.
Which is better for small businesses: ERP or CRM?
The choice between ERP and CRM depends on a small business’s core needs:
- ERP: Best for businesses looking to streamline operational processes, manage inventory, and handle financials more effectively.
- CRM: Ideal for those focusing on boosting sales performance, enhancing customer service, and improving customer relationship management.
Is ERP more expensive than CRM?
Typically, ERP systems are more expensive than CRM solutions due to their broader range of functionalities and complexity. However, costs vary based on the specific features and vendors. ERP’s comprehensive scope generally leads to higher implementation and maintenance costs.
Do I need both ERP and CRM for my business?
The need for both systems depends on your business objectives. Integrating ERP and CRM can be advantageous if you require robust operational efficiency and superior customer management. This integration ensures comprehensive coverage of both internal processes and customer interactions.
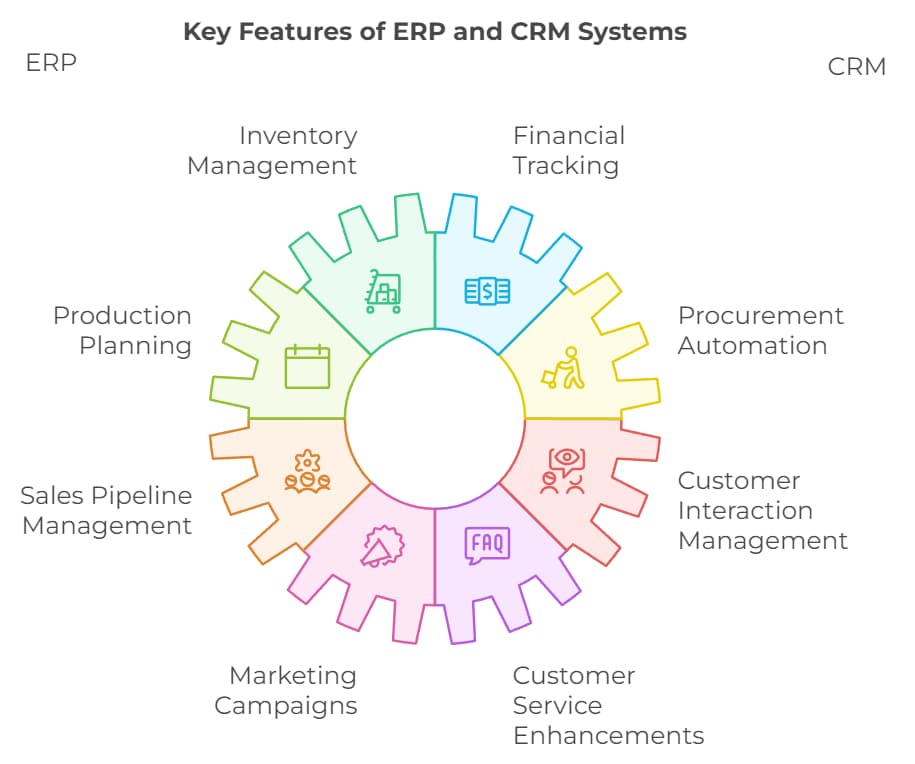
What are the key features of ERP systems?
Key features of ERP systems include:
- Inventory Management: Tracks stock levels, orders, and supply chain logistics.
- Financial Tracking: Manages accounting, budgeting, and financial reporting.
- Production Planning: Schedules and oversees production processes.
- Procurement Automation: Streamlines purchasing and supplier management.
What are the key features of CRM systems?
CRM systems typically offer:
- Sales Pipeline Management: Tracks sales leads and opportunities.
- Customer Interaction Management: Records and manages customer communications.
- Marketing Campaigns: Facilitates and monitors marketing efforts.
- Customer Service Enhancements: Provides tools for better support and engagement.
Can ERP systems help with customer relationship management?
While ERP systems can store customer data, they lack the specialized tools for sales and marketing that CRM systems provide. CRMs are designed to offer more in-depth customer relationship management capabilities, making them essential for enhancing sales processes and customer interactions.
How long does it take to implement ERP or CRM?
Implementation times vary:
- CRM Systems: Generally faster to deploy, with implementation often taking a few weeks.
- ERP Systems: More complex and time-consuming, with implementations typically spanning several months due to their broad scope and integration requirements.
How do I decide whether to implement ERP, CRM, or both?
Consider these factors to make an informed decision:
- Immediate Needs: Identify whether your focus is on operational efficiency (ERP) or customer management (CRM).
- Budget: Evaluate your financial resources and how they align with the costs of each system.
- Long-term Goals: Determine if you need comprehensive integration of both systems to support future growth and operational complexity.