ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) and PLM (Product Lifecycle Management) are two distinct systems that address different needs in business management. ERP systems focus on integrating and automating core operational processes such as inventory and financial management, aimed at enhancing overall efficiency. On the other hand, PLM systems manage the entire lifecycle of a product, from design to end-of-life, emphasizing product development and innovation.
By comparing ERP and PLM, businesses can better understand which system aligns with their goals, whether they seek to optimize daily operations or advance product management strategies
Understanding ERP and PLM
To understand the differences between ERP and PLM better, you first need to understand the main areas of operation of these solutions.
What is ERP?
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) integrates a wide range of business processes into a unified system, streamlining operations across various departments. For small and medium-sized businesses, ERP systems are invaluable for automating tasks such as inventory management, order processing, and financial reporting. By centralizing data and workflows, ERP solutions enhance operational efficiency, reduce redundancies, and support informed decision-making.
These systems offer real-time insights into key performance indicators, facilitating better resource allocation and process optimization. As a result, businesses can manage their entire operation more cohesively, improving overall productivity and responsiveness.
What is PLM?
PLM (Product Lifecycle Management) manages the complete lifecycle of a product, from initial concept through design, manufacturing, and eventual retirement. It centralizes all product-related information and processes, fostering collaboration across teams and stages. PLM systems are crucial for driving innovation by providing tools for detailed product design, change management, and compliance tracking. By streamlining product development workflows and maintaining comprehensive data, PLM enhances the ability to bring new products to market efficiently and effectively.
This system supports continuous improvement and adaptability, ensuring products meet market demands and regulatory requirements throughout their lifecycle.
What Is Kladana ERP?
Intuitive User Interface
Get up and running with our cloud-based, all-in-one ERP solution in just 15 minutes. No software installation or lengthy forms required.
Maximize Your Profit
Minimize expenses, deter warehouse losses, pinpoint your market niche, and boost sales — all achievable through a single, streamlined platform.
Transparent Operations Management
Track every step of your workflow: from orders and transactions to documents, costs, and user activity, with every detail captured.
Comprehensive Reports and Insights
Leverage pre-built reports, apply filters for precise data, automate report generation, and have fresh insights delivered straight to your inbox.
Dedicated Support
Our onboarding expert will guide you through 1–3 personalized sessions to help configure your settings. Need help? Our support team will resolve your issues or answer questions within 5–15 minutes during business hours.
Built-in App Marketplace
Easily activate the Online Order App to start selling without a website and create custom catalogs for different customer groups.
Key Differences Between ERP and PLM
Explore the basic distinctions between the described software solutions.
Focus and Scope
- ERP systems concentrate on integrating and managing operational processes across various business functions. Their primary focus is on streamlining tasks such as inventory control, financial management, and order fulfillment. This comprehensive approach helps businesses optimize overall operational efficiency and resource allocation.
- PLM systems, on the other hand, oversee the entire lifecycle of a product, from conception through design and manufacturing to retirement. Their emphasis is on enhancing product development, ensuring quality, and managing changes throughout the product’s life. While ERP addresses general business operations, PLM specializes in detailed product management and innovation.
Integration and Functionality
- ERP systems are designed to unify various business processes, making them suitable for managing supply chain activities, financial transactions, and inventory management. They provide a centralized platform for operational data and workflow automation.
- PLM systems integrate product-related processes, such as design, compliance, and lifecycle management. They facilitate detailed product data management and support cross-functional collaboration, particularly in product development and innovation.
Target Users and Applications
| Aspect | ERP | PLM |
Target Users |
|
|
Primary Use |
|
|
Applications |
|
|
This comparison highlights how ERP and PLM serve distinct roles but can be complementary depending on specific business requirements.
How ERP and PLM Work Together
Combining ERP and PLM systems can transform how businesses manage their operations and product lifecycles, offering a more integrated approach to business management.
Benefits of Integration
Integrating ERP and PLM systems can significantly enhance business operations by bridging the gap between product development and operational management. This integration allows for seamless data flow between the two systems, reducing manual data entry and improving accuracy.
Businesses benefit from unified insights into product information and operational metrics, leading to more informed decision-making. Enhanced collaboration across departments is another advantage, as product design and supply chain teams can access consistent, up-to-date information.
The result is:
- Streamlined processes
- Reduced errors
- Improved efficiency
Making it easier to respond to market changes and manage complex product lifecycles effectively.
Use Cases for Combined Systems
Integrating ERP and PLM systems proves advantageous in various scenarios:
- Complex Manufacturing Environments: In industries with intricate manufacturing processes, such as aerospace or automotive, combined ERP and PLM systems offer robust solutions for managing detailed product data alongside supply chain logistics.
- Companies with Extensive Product Lines: Businesses with broad product portfolios benefit from integration by ensuring that product development, inventory management, and order fulfillment processes are synchronized, reducing delays and improving overall operational coherence.
These use cases illustrate how ERP and PLM integration supports efficient and scalable business operations.
ERP vs PLM for Different Business Needs
Choosing between ERP and PLM systems often depends on the specific needs and goals of a business. Each system offers distinct advantages tailored to different aspects of business management, from operational efficiency to product lifecycle oversight.
ERP for Small Businesses
ERP solutions are tailored to meet the specific needs of small businesses by offering a range of benefits that include automation, cost-efficiency, and scalability. For small businesses, ERP systems streamline essential operations such as accounting, inventory management, and customer relationship management, providing a centralized platform for various tasks. This automation reduces manual efforts and errors, which can be particularly beneficial for businesses with limited resources.
- Cost-Efficiency: ERP systems help small businesses manage costs effectively by integrating financial processes and offering real-time insights into expenses and revenues.
- Scalability: Small businesses can start with basic modules and scale up as their needs grow, avoiding the upfront costs of more extensive systems.
- Automation: By automating routine tasks, ERP systems free up time for employees to focus on strategic activities.
PLM for Manufacturers
PLM systems address the unique needs of manufacturers by managing comprehensive product data, enhancing collaboration, and supporting innovation throughout the product lifecycle.
- Product Data Management: PLM systems provide a central repository for product information, enabling manufacturers to track changes, ensure accuracy, and maintain consistency across departments.
- Improved Collaboration: By facilitating communication between design, engineering, and production teams, PLM systems enhance teamwork and accelerate time-to-market.
- Support for Innovation: PLM systems enable manufacturers to manage new product development efficiently, from concept through production, fostering innovation.
ERP vs PLM for Product Management
ERP and PLM systems both play crucial roles in product management but in different capacities:
- ERP: Focuses on product inventory, order processing, and overall supply chain management. It provides tools for tracking inventory levels, managing production schedules, and processing orders efficiently.
- PLM: Specializes in product development and lifecycle management, offering features for managing design changes, compliance documentation, and product performance throughout its lifecycle.
| Aspect | ERP | PLM |
Focus |
|
|
Functionality |
|
|
Outcome |
|
|
ERP vs PLM for Supply Chain Management
ERP and PLM systems each contribute to supply chain management in distinct ways:
- ERP Systems: Enhance supply chain efficiency by integrating procurement, inventory management, and logistics. They provide real-time visibility into supply chain operations, facilitating better planning and coordination.
- PLM Systems: Improve supply chain collaboration by ensuring that product data and specifications are shared accurately across the supply chain. This integration helps in aligning production schedules with design updates and managing supplier relationships effectively.
These insights demonstrate how ERP and PLM systems address different aspects of business needs, offering complementary benefits based on the specific requirements of each organization.
Read‑alikes
ERP Inventory Management: 12 Benefits for Your Business in Full Guide
MRP vs ERP: A Comprehensive Guide to Business Management Solutions
Top 20 ERP Software for SMEs in India and Across the World 2025
Choosing Between ERP and PLM
Selecting between ERP and PLM systems requires a thorough understanding of how each aligns with your business needs, objectives, and industry requirements. Making the right choice can significantly impact your operational efficiency and product management capabilities.
Which is Better for Your Business?
Deciding whether ERP or PLM is better for your business depends on your primary goals and the challenges you face. If your focus is on improving overall operational efficiency, streamlining processes, and managing resources effectively, an ERP system is likely the better choice. ERP solutions are designed to integrate various business functions into a unified system, which enhances productivity and reduces costs.
Conversely, if your primary goal is to manage the entire lifecycle of your products—from design through manufacturing to end-of-life—PLM is the more suitable option. PLM systems are tailored to handle detailed product data, support collaboration across teams, and drive innovation.
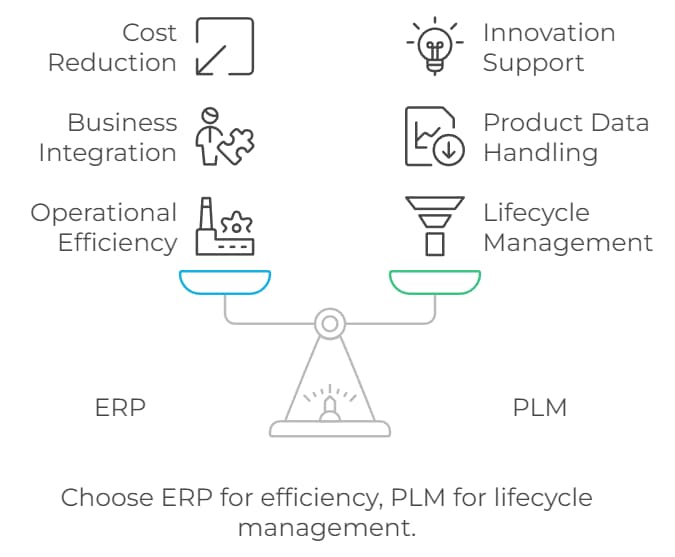
Factors to Consider in Your Decision
When choosing between ERP and PLM, consider the following key factors:
- Budget: ERP systems are generally more cost-effective for small to mid-sized businesses due to their broad functionality and scalability. PLM systems, with their specialized focus, can be more expensive but offer deeper capabilities for managing product development.
- Business Size: Small businesses may find ERP systems more aligned with their needs for integrated operations and financial management. Larger organizations with complex product lines might benefit more from PLM systems that offer advanced product lifecycle management.
- Complexity of Business Processes: If your business involves complex product development and innovation, a PLM system will provide the tools needed for effective management. For businesses with simpler processes, an ERP system might suffice to handle operations efficiently.
Frequently Asked Questions on ERP vs PLM
To address common inquiries about ERP and PLM systems, this section provides clear answers to frequently asked questions.
What is the main difference between ERP and PLM?
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems focus on automating and integrating business processes across various departments, such as finance, HR, and supply chain, to enhance operational efficiency. In contrast, PLM (Product Lifecycle Management) systems are designed to manage the entire lifecycle of a product — from initial design and development through to manufacturing and eventual retirement. While ERP improves overall business processes, PLM zeroes in on product data and development.
Can ERP and PLM systems be integrated?
Yes, integrating ERP and PLM systems can create a comprehensive view of both business operations and product data. This integration enhances efficiency by ensuring that information flows seamlessly between systems, improves data accuracy, and supports better decision-making. It allows businesses to synchronize product-related data with operational processes, leading to more informed and agile responses to market changes.
How does ERP benefit small businesses?
ERP systems provide significant benefits for small businesses by automating routine tasks, such as inventory management, order processing, and financial reporting. This automation reduces manual errors and administrative overhead. Additionally, ERP systems offer valuable insights through data analytics, which supports strategic decision-making and helps small businesses improve efficiency and scalability.
What role does PLM play in product development?
PLM systems are crucial in product development as they manage all aspects of the product lifecycle. They facilitate collaboration among different teams, streamline the development process from concept to market, and ensure that product data is accurate and up-to-date. This comprehensive management helps accelerate time-to-market and supports innovation by coordinating design, manufacturing, and product updates.
Is ERP or PLM better for supply chain management?
ERP systems are generally more effective for overall supply chain management due to their ability to integrate various business functions, including procurement, production, and logistics. They offer a holistic view of supply chain activities. However, PLM systems contribute to supply chain management by providing detailed product information, which helps in aligning product development with supply chain requirements.
How do I decide whether to use ERP or PLM?
The choice between ERP and PLM depends on your business needs. If your focus is on streamlining and automating overall business processes, ERP is likely the better choice. On the other hand, if managing the product lifecycle and enhancing product development is your priority, PLM will better meet those needs. Consider your primary objectives and the complexity of your operations when making this decision.
What are the cost implications of implementing ERP vs PLM?
ERP systems typically involve higher implementation costs due to their broad functionality and integration requirements. They offer extensive capabilities across various business functions. PLM systems, while potentially less expensive, focus on specialized product management features, and their costs can vary based on the complexity of the features required for effective product lifecycle management.
Can small businesses benefit from PLM systems?
Yes, small businesses can benefit from PLM systems, particularly those involved in product development and innovation. PLM systems help by improving product management, enhancing collaboration across teams, and streamlining the product development process. Even small businesses can leverage these systems to gain a competitive edge in managing their products more efficiently.
How do ERP and PLM impact inventory management?
ERP systems offer robust inventory management capabilities, including tracking stock levels, managing orders, and optimizing inventory turnover. PLM systems support inventory management by providing accurate and comprehensive product data, which aids in better forecasting and inventory planning throughout the product lifecycle.
What are the long-term benefits of integrating ERP and PLM?
Integrating ERP and PLM systems delivers long-term benefits such as improved data accuracy and consistency, enhanced collaboration across departments, and greater overall efficiency in managing both business operations and product lifecycles. This integration allows businesses to synchronize processes and data, leading to better decision-making and a more agile response to market demands.


