The global enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems market is enjoying an unprecedented boom. In 2019 it was worth $39 billion, a number that’s expected to rise to $86 billion by 2027 according to Allied Market Research. ERP solutions gained popularity thanks to advancements in cloud technology. Businesses can now shift off-site, using automated solutions for streamlining and optimizing operations almost everywhere.
In this article, we’ll explain what ERP systems are and how they improve productivity and decision-making for business owners. We’ll also look at real-life examples of modern ERPs and give tips for selecting the right solution. This will help those looking to use ERP systems for their business growth.
If you’re choosing the best ERP solution for your business right now, check out the roadmap created by our expert. There you’ll find the list of necessary actions and their descriptions formatted as a customizable table.
What Is the Definition of ERP?
ERP system is a multifunctional software that helps organizations manage and improve their essential processes. It brings together different aspects like finance, HR, inventory, manufacturing, retail, wholesale, procurement, etc.
ERP helps the staff from different departments work better together and access information instantly. ERP systems boost productivity, cut costs, and save precise business data by means of automated functions. They’re a vital tool for businesses to run smoothly and stay competitive.
🧊 4 Free Inventory Ckecklists
Learn how to manage stock, set up your warehouse, track barcodes, and build product cards for e‑commerce — even if you’ve never done it before
✅ Inventory management
✅ Warehouse setup
✅ Barcode tracking
✅ E-commerce product cards
Why Is an ERP Solution Important?
For companies taking the first step from Excel to a specialized solution, it is quite difficult to figure out/set up everything and train employees on their own so that everything works quickly. Also, the business wants to see fast results: today we set up stock management and enter the data, and tomorrow we will focus on ERP, rather than Excel when analyzing stock. There is no time or money to plan for a long time or to implement for a long time.
The ERP can be compared to a space flight control center, where all information about the project is accumulated. The ERP system plays a critical role in every department of the company. Thanks to it, customers receive the necessary goods and services on time, the warehouse is timely stocked with the materials or products, counterparties receive payments, and fiscal authorities get the necessary reporting.
In addition, modern ERPs are capable of providing reports and analytical data that previously took employees a lot of time and effort to prepare, only in a few clicks. Converting large amounts of information into easy-to-read reports allows business owners to make management decisions, and forecasts and plan specific processes faster and more precisely.
Here’s an example that highlights the importance of an ERP system for a manufacturing company:
XYZ Manufacturing Company produces industrial machinery and equipment. Before implementing an ERP system, they faced several operational challenges:
| Challenge | Result after ERP Launching |
| Inventory Management | |
The company had multiple warehouses, making it difficult to track and manage inventory accurately. This resulted in overstocking of some items and shortages of critical components, leading to increased costs and production delays. |
With the ERP system, the company gained real-time visibility into inventory levels across all warehouses. Now it is possible to track stock levels and monitor usage patterns. The results are optimal inventory levels, reduced carrying costs, and fewer production delays. |
| Production Planning | |
Without real-time visibility into inventory levels and customer orders, production scheduling was erratic. This resulted in inefficient use of resources and missed delivery deadlines. |
The ERP system allowed the company to integrate sales orders and production schedules, enabling efficient resource allocation and better planning. Production can now be aligned with customer demand, reduce idle time, and improve on-time deliveries. |
| Financial Management | |
The financial department struggled with manually reconciling data from different departments. This resulted in errors in financial statements and difficulties in making informed decisions. |
The ERP system integrates financial data from various departments. This led to accurate financial reporting, improved decision-making, and enhanced control over the company’s finances. |
| Communication | |
Departments operated independently, with limited communication and collaboration between them. This hindered the exchange of critical information. |
The ERP system facilitated seamless communication between departments through a centralized platform. Employees could access the same data, collaborate on projects, and share information easily, enhancing overall efficiency and teamwork. |
As a result of implementing the ERP system, XYZ Manufacturing Company experienced reduced operational costs, improved customer satisfaction due to on-time deliveries, and increased overall productivity.
How Does it Work?
A common database and modules that can interact with each other are the core elements of any ERP system. Businesses can launch an ERP with a basic set of modules and purchase new ones if necessary. However, sometimes It is quite conventional to divide the entire ERP system into modules because everything is included at once.
But businesses can start using ERP for some tasks, for example, control of purchases and sales, and then expand their use, purchasing additional modules if necessary.
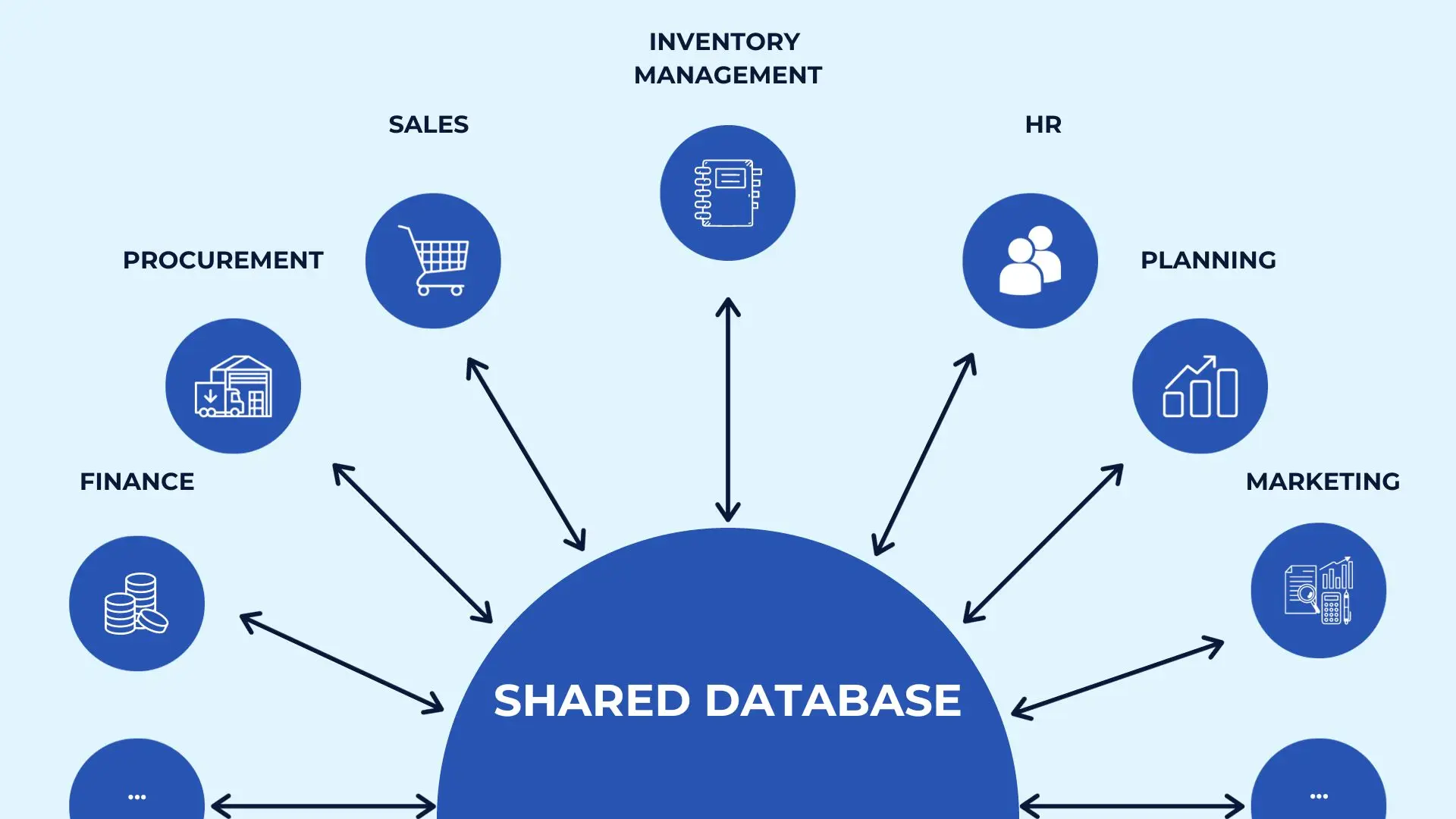
Information entered into the module by one user instantly becomes available to everybody in the company. This helps employees stay informed, make better decisions, and adapt to changing conditions.
A perfect ERP system is one that can offer a relevant module for each business process. Company employees, in turn, should provide data entry on time. In this case, ERP will be able to bring maximum benefit.
What Are the Common ERP Modules?
ERP solutions usually include several different software modules, which are bought individually according to the need to manage certain processes and functions. Each ERP module focuses on different aspects of business.
Common ERP modules cover tasks like inventory management, product planning, procurement, sales, finance, marketing, and human resources. Here is the list of the widely used ERP modules:
Manufacturing Module
A central part of the ERP software. Its main job is to simplify complex manufacturing processes and ensure that production matches demand. This module typically includes material planning, production scheduling, creating BOMs and production orders, managing manufacturing, quality control, and more.
Inventory Management Module
This module is aimed at monitoring materials, semi-finished, and finished goods at stock premise. It can manage the prices and make unit cost calculations, issue catalogues, synchronize stock with production and shipment, and generate barcodes, batches, serial numbers, and SKUs.
Procurement Module
The module helps businesses buy needed amounts of materials and services. It automates purchasing by issuing purchase orders, invoices, and other documents, and managing returns.
Sales Module
The sales module helps to establish efficient communication with customers. It uses data to boost sales and find the best deals. It manages orders, lifecycles of goods, contracts, and billing, supports sales teams, and generates sales reports.
Accounting and Finance Module
This module is used by businesses of all kinds. It effectively closes the books, creates financial reports, helps manage financial risks, and tracks accounts receivable and accounts payable.
HR Module
The Human Resources module in the ERP system manages everything related to personnel, jobs, and careers, like hiring, payroll, and attendance. It can also handle other important tasks. It helps businesses switch from manual HR methods to automated processes.
Relative Case Stories
Unicorn Natural Products Manufacturing: a Journey from Spreadsheets to ERP
Artisanté: How to Streamline Chocolate & Coffee Manufacturing Management in Half a Year
Cura Pharmaceuticals Manufacturing: Increased Data Accuracy & Business Workflows in 6 Months
10 Key Reasons to Switch to ERP
In India, even small companies want to work with specialized solutions instead of Excel and notepads. Several years ago it was okay to store documents in folders on a PC, keep records in Excel, and organize communication and processes exclusively via email/messengers and talks. Now this is no longer convenient for business. Too much time needs to be spent on checking, but still, the doubt remains. Are the records really up-to-date? Are all tasks accurately completed?
In order to give you vivid examples of how ERP systems help businesses in achieving their goals and solving problems we will introduce you to Mr. Kumar. He runs a small jewelry-making business. Let’s see how ERP helps him cope with difficulties.
Reason 1. Cost Saving
The introduction of an ERP system can save a lot of money for business owners. Many operational, administrative, and capital costs can be lowered or eliminated with the help of automation the solution provides. For example, the ERP software usually puts an end to manual data entry and some kinds of routine paperwork.
An ERP solution gives businesses the ability to evaluate the budget and find the weak spots where they are spending too much money. This makes it easier to reduce spending generally and helps to plan things better, so one doesn’t waste money in a rush.
😟 Problem: Mr Kumar’s business was facing high operational and administrative costs due to manual data entry and routine paperwork. This manual process was time-consuming and prone to errors, leading to increased expenses.
😇 Solution: The introduction of an ERP system helped the company significantly reduce costs. The ERP software automated data entry and eliminated the need for manual paperwork. By streamlining these processes, the business saved both time and money. Additionally, the ERP system allowed Mr. Kumar to evaluate the budget and identify areas where excessive spending was occurring.
Reason 2. Simplified Reporting
ERP systems make it easy to generate reports, allowing managers to promptly use valuable insights to enhance their real-time performance. Effective reporting is a crucial experience for making intelligent decisions based on data.
Reason 3. Single Source of Information
ERP systems keep all of a company’s data on a single platform and preserve it from damage and duplication. This also guarantees that any modifications made by users in every area are immediately updated in the database. All employees have access to the content and can easily track who changed existing records or created anything new.
Reason 4. Easier Compliance
Businesses often struggle to meet compliance standards, which can be a challenging and ongoing task. Achieving complete accuracy in financial records is no simple feat. Ensuring regulatory compliance becomes easier with a single source of truth. ERP systems are also a great help in achieving regulatory compliance due to pre-built reports.
😟 Meeting regulatory compliance standards in the jewelry-making industry was a complex and ongoing task for the company, especially in maintaining accurate financial records.
😇 Mr. Kumar found it easier to achieve regulatory compliance with the ERP system. The ERP software offered pre-built reports that helped in maintaining accurate financial records and meeting compliance standards.
Reason 5. Scalability
Modern ERP systems can grow together with the companies that use them. They have the ability to scale in different spheres including markets, locations, and a variety of goods. Cloud ERPs swiftly and securely adapt to new conditions and technologies and help businesses increase.
Reason 6. Data Security
Data is one of the most important business assets. It plays a crucial role in decision-making and should be kept away from strangers’ eyes. ERP software protects valuable information. It replaces spreadsheets and files stored on employees’ computers or mobile phones and sent online via email in the past with one single source of truth. For extra safety, in a cloud ERP system, data is spread across many remote servers, preventing a single point of failure.
Reason 7. Risk Management
ERPs enhance data security by controlling who can access and change data. To minimize the chances of fraud and other illegal and harmful activities these solutions have simple permission settings, ensuring that employees only access the necessary information.
😟 The company needed to minimize the risk of fraudulent activities and ensure that employees only accessed the necessary information.
😇 The ERP system implemented permission settings to control data access. Now Mr. Kumar can be sure that only authorized employees can access and modify data. Any suspective activity immediately becomes visible to him.
Reason 8. Enhanced Customer Service
In any market segment, businesses must try to be better than competitors in order to win the attention of the target audience. Customer service plays one of the most important roles in the field of building a sales system. If the buyer is dissatisfied, even the best product risks remaining unclaimed. An ERP system can help with this. It stores all customer information in one place, making it easier to provide quick and personalized support.
Furthermore, an ERP system also helps by making sure orders are accurate and delivered on time. Software indirectly keeps customers satisfied and encourages them to come back with new orders.
😟 Providing excellent customer service was crucial for Mr. Kumar’s jewelry-making business to stand out in a competitive market. Managing customer information and ensuring accurate, on-time deliveries were challenges.
😇 The ERP system gathered all the customer information in one place. Managers now can quickly react to any customer problem, provide quick support, and resolve the issue or report to their boss.
Reason 9. Improved Interdepartmental Collaboration
After launching the ERP system all the departments of the company start using similar or the same interfaces in their daily work. They can view the data created by other colleagues and watch important processes and events without messaging or calling them and asking to share the information required. This makes business processes transparent and swift.
😟 Mr. Kumar’s employees often had difficulties getting information from other colleagues. Everyone was busy and didn’t want to waste time explaining or sending documents. It led to conflicts, besides, the processes were slowing down.
😇 After implementing the ERP system, all departments within the company used similar interfaces for their daily work. Now they can access data created by colleagues and monitor important processes and events without the need for constant messaging or calling for information sharing.
Reason 10. Precise Forecasting
A business can prepare for new market conditions if it carefully analyzes all trends and knows what changes to expect. This can be achieved through forecasting. An ERP solution increases the accuracy of forecasts since it stores all the data on the dynamics of inventories, production, sales, depreciation, and other important indicators.
😟 Mr. Kumar experienced a lack of information and time to prepare for new market conditions and make accurate forecasts to help a business grow.
😇 The ERP system improved forecasting accuracy by storing data on inventory dynamics, production, sales, depreciation, etc, and making corresponding reports. This data consolidation enabled businesses to analyze trends and make more precise forecasts.
The overall situation is connected to the acceleration of economic processes, and increased requirements for efficiency and speed of work. When a client places an order, they no longer want to wait several days while the entrepreneur analyzes the data and finds out whether and in what time frame they can deliver the goods. In the case of working with marketplaces, it is even stricter: goods must be produced and shipped according to a clear schedule, otherwise, one simply won’t receive the required volume of orders anymore.
Types of ERP deployment
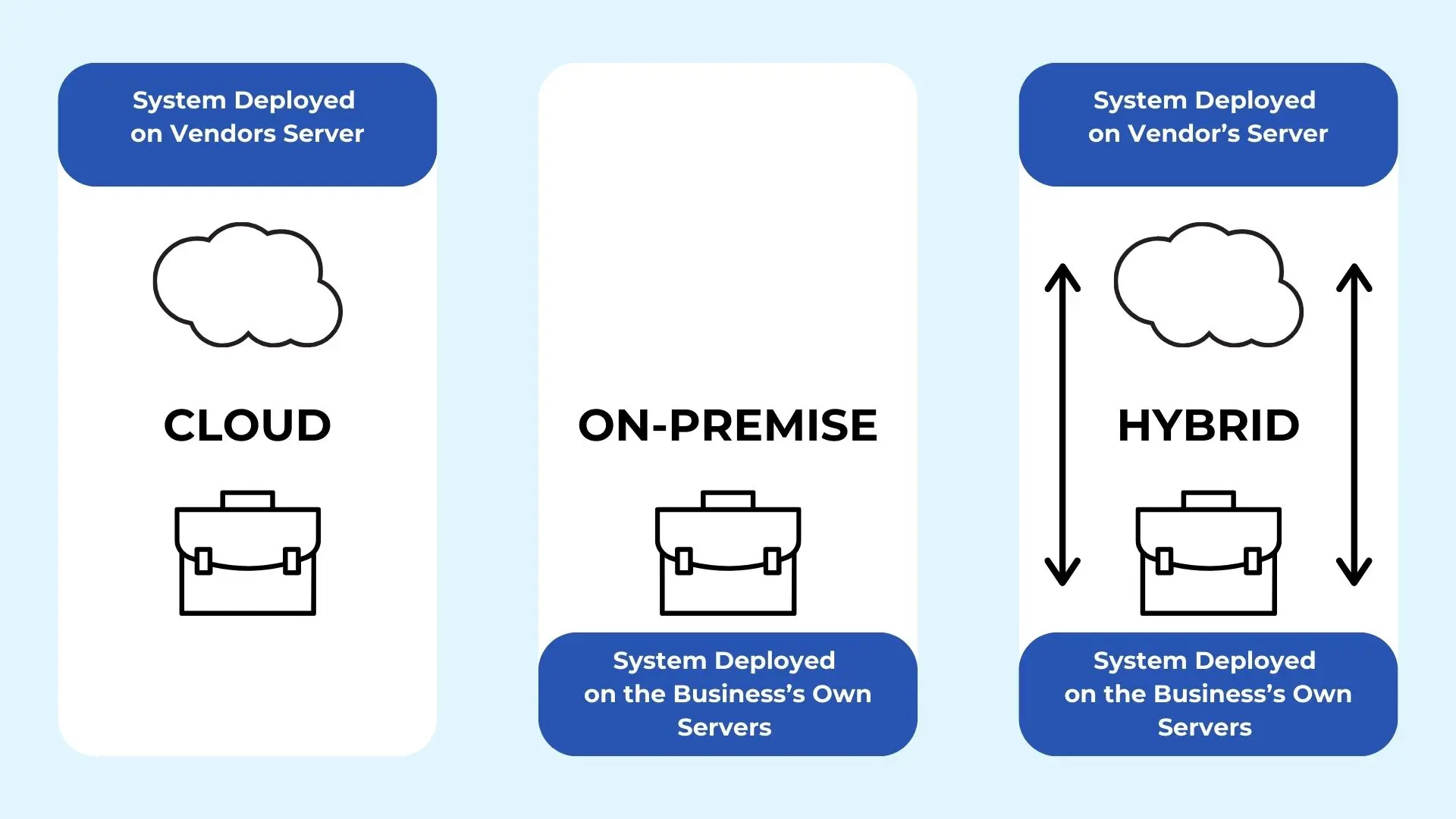
ERP solutions can be ranged according to the method of deployment, including on-premise implementation, public and private cloud hosting, and versatile hybrid setups that integrate these environments. In this paragraph, we will explain how each ERP type operates:
On-premise ERP
The on-premise ERP system can only be used on the business’s own servers and devices. The business maintains and updates the software and network on its own. Most often, on-site solutions are purchased and installed by large enterprises that have the ability to independently store the information, support the operations, hire IT experts, and pay for servers.
Examples: PACT ERP, IFS, Microsoft Dynamics 365.
Cloud-Based ERP
Cloud ERPs are deployed on the ERP vendor’s servers. The client’s impact is minimal. He does not need to update and maintain it himself; all he needs is Internet access and a web browser. This way, clients are not tied to a certain address, they can work with ERP globally and on different devices, and all the information about business processes is at his fingertips.
Examples: Kladana, PACT ERP, NetSuite ERP, Zoho One, Focus.
Start your acquaintance with the cloud-based systems with Kladana — an ERP for small and medium-sized businesses. It’s time to take control of your inventory, sales, and manufacturing.
There are several options for cloud ERP, here are the most common of them:
True Cloud Solution
This is a multi-tenant system deployed on the cloud. The ERP vendor manages the server and all processes connected with the maintenance, updates, and backups of the software on his own. He gives remote access to the ERP solution to his clients and stores their information in data centers connected to servers preserving their privacy. The hosting cost is divided among many clients, so this system is less expensive than the others.
Hosted Cloud Solution
It is a single-tenant solution. It means that all client information is deployed on a private cloud. Such systems allow control of the data with enhanced remote access and the possibility of emergency recovery and offer extended security and broadened data management possibilities.
Hybrid ERP
Hybrid ERP combines on-premise and cloud setups. One of the variants is called two-tier ERP, where a company uses on-premise ERP at its main office but uses cloud systems for branches. The cloud solutions are connected to the main ERP used for the headquarters. Some companies use cloud systems for certain tasks but keep on-premise software for other processes.
No matter what, it’s essential to connect the cloud systems with the on-premise solutions to keep information flowing smoothly. This can be quite tricky in practice, even though it sounds simple.
Examples: TallyPrime, PACT ERP, Sage 300, IFS, Microsoft Dynamics 365.
Open-source ERP
Open-source ERP solutions offer companies freely available source code as a starting point. They can adapt the code to suit their particular needs. It’s a common practice that open-source ERP vendors offer their software for free. A small yearly fee is charged only if businesses want to use the cloud.
However, the support you get from these providers is limited, and it’s up to you to set up and improve the functionality of the system. This means you’ll need to hire somebody who knows how to work with the software. Like other open-source programs, this ERP solution is a low-cost or even free option that can be a good fit for some companies.
Examples: ERPNext, Odoo, Flectra, Dolibarr.
ERP Solutions by Business Size
The size of the business is one of numerous factors influencing the choice of the best ERP. However, no system will perfectly suit a large or small company. But for each size, there are preferred functions that you should pay attention to when choosing an ERP solution. Let’s look at them in this paragraph:
ERPs Suitable for Small Businesses
When small businesses plan their software needs, they should avoid systems that have more features than necessary. This helps save money and reduces the training required for employees. However, the chosen system should be capable of expanding and supporting new processes and growth over time. It should also have an easy setup process.
That’s why cloud-based ERP is often the best choice for small businesses. It has lower initial costs, a faster setup, and requires fewer technical resources compared to on-premise or hybrid options. The cloud can grow with the business, and a good provider can add modules and features as needed.
Best ERPs for Medium-Sized Businesses
Medium-sized companies should find an ERP that offers a sufficient variety of features to support all their day-to-day business processes. Like smaller companies, they should choose a vendor who can offer a solution that will grow along with their future needs.
Many medium-sized organizations don’t have enough IT personnel. That’s the reason why cloud ERP software is so popular in this group. It’s not only cheaper at the start, but it’s also more manageable for companies with limited technical skills. However, if a medium-sized business needs multiple customizations or has to follow strict data storage rules, it’s better to opt for on-premise or hybrid solutions or cloud-based systems with API.
Enterprise ERP
Big business leaders should choose software that supports all the functions of their companies. Corporations need systems that can handle lots of data and meet the needs of different business units. Only few ERP vendors can offer such solutions.
Many enterprises prefer on-premise or hybrid systems because they had installed their ERPs long before cloud solutions appeared. Moving a large ERP system to the cloud can be time-consuming and costly. However, big businesses are making this move to reap the benefits and prepare their workflows for potential growth. Some enterprises also use a two-tier ERP approach, combining a cloud solution with their primary on-premise ERP system.
| Business Size | Preferred ERP Solution | Key Considerations |
| Small businesses | Cloud-based ERP | |
| Medium-sized Businesses |
|
|
| Enterprises |
|
|
The future of ERP
ERPs are increasingly becoming not so much databases with records of the movement of resources, but rather a single point of assembly of all the necessary processes. ERP is no longer just ERP, but a single window for business management. If we look under the hood, we can see built-in modules or integrations: OMS, CRM, WMS, payment systems, integrations with shopping carts and marketplaces, task manager, etc.
Vertical Extensions & Integration
Earlier users had to choose between the most efficient ERPs and integrated ones. Businesses seeking the combination of the advantages of both types may inspire the creation of comprehensive solutions seamlessly incorporating full integration and vertical extensions. In this case, they will get all the needed functions without the headaches of problematic integration.
Such comprehensive solutions will include the ability to customize a dashboard and select exactly those functions that will be in demand by each employee. He will have the necessary features at hand in a separate menu. This will make it easy and quick to train managers specifically for their tasks.
More Simplicity for Users
All the participants of the D2C scheme share a common desire for a tailored software decision that can adjust to their unique requirements and help them save time and other resources for other activities. Nowadays various industries including manufacturing are continuing to search for the most user-friendly solutions with minimal share of code. They opt for simple software their employees can master in a short time. So, we have all the chances to enjoy ERPs with personalized control panels, chat services, and working processes in the near future.
According to Paul Saunders, head of product strategy for SAP S/4HANA, future ERPs won’t replace the human component at work but will help users make better decisions: «It’s human intelligence and artificial intelligence coming together». People will adapt the system to their own requirements using «intelligent connectivity», Saunders said.
Cloud-basing Is a Must
Ubiquitous access to the Internet allows more and more business owners to enjoy the benefits of cloud software. One no longer needs to be stuck at their PC to get access to data and manage the business processes. Compared with the on-premise solutions cloud-based ERPs offer enhanced security and lesser cost of support, more possibilities for integration. Supply follows demand: as of 2023, according to the data collected by technology market research company Apps Run the World the cloud solutions market is valued at approximately $ 153.6 billion. The amount increases annually and by 2025, it is expected to grow to 168.6 billion.
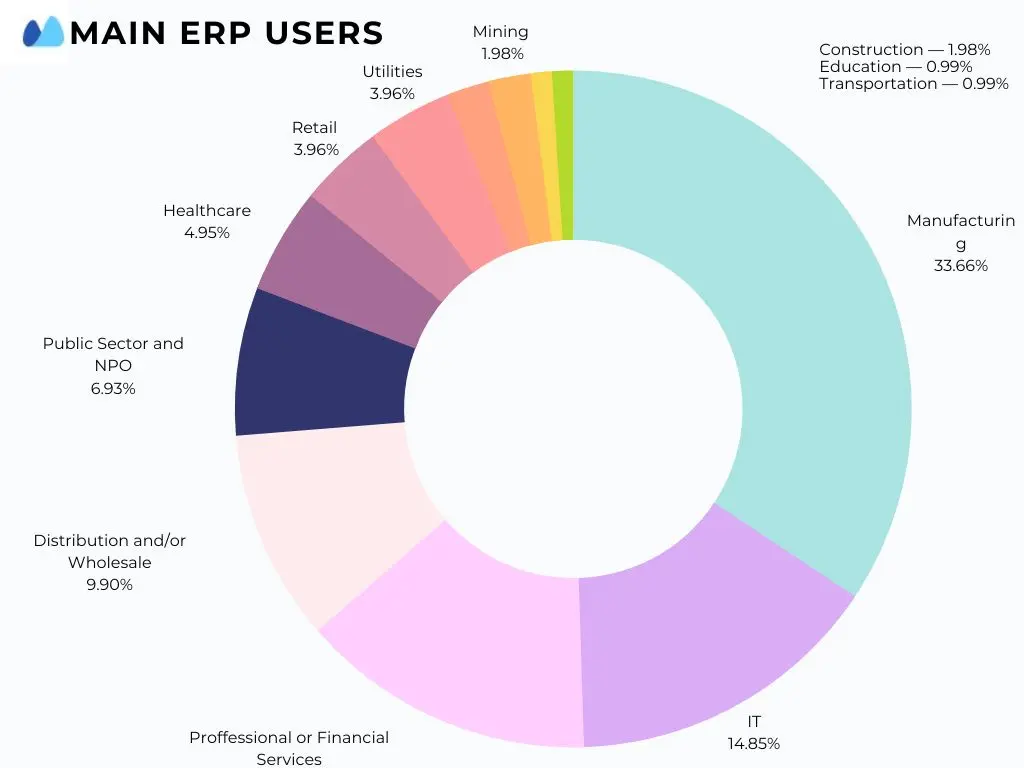
What industries use ERP?
Read our case story and learn how 1,500 bottles of lemonade are moved from one warehouse to another in two clicks.
According to the source, mentioned in the previous paragraph, the global ERP software market continues to grow.
ERP solutions are gaining popularity among businesses representing every industry. To meet growing demand EPRs discover more and more features satisfying the needs of the clients from different industries.
Here we will name the industries that use Enterprise Resource Planning systems to manage their business processes:
Selecting the Right ERP Solution
Businesses in India are choosing ready-made solutions over half-finished ones with the individual modification option. As a rule, the companies that are trying to manage processes in a specialized solution for the first time, at the start don’t know how exactly things should work. They simply cannot formulate requirements that will be relevant for the next one-three years.
Starting to work on a ready-made solution, you gradually come to understand what functions need to be adjusted. Sometimes the working processes themselves are revised.
The modern market offers many ERP solutions that differ in the set of available functions, price, interface, plans, level of vendor support, and other various factors.
Choosing the right ERP is not a simple process and may raise a lot of questions, but it can be divided into understandable short steps. This will make things easier and help to get started faster. Whether you need to select the first ERP system or to find a suitable replacement, we recommend you make a roadmap. Things will get clearer, and you won’t need to hire a professional. Check out the roadmap example we created for you. Make a copy and mark the finished phases or edit it according to your own needs.
You can also use the following tips while planning:
-
Don’t be guided only by a brand name. Companies frequently make decisions regarding their software solutions based on either brand recognition or the choices of their competitors. This approach might seem convenient, but it’s not always the best practice and strategy. It’s better to focus on what suits their needs and competitive edge.
Despite the dominance of a few well-known software vendors in terms of market share, the landscape is more diverse than it appears. There are dozens of other ERP software options on the market. Each of these solutions offers different features and possesses unique strengths, catering to different business needs and niches.
-
Identify what your business needs in an ERP system. For the successful implementation of the new solution, it’s vital to learn what features your business needs. If you’re starting anew, do a detailed research. Identify the processes the ERP will work with both independently and together with other systems. If you’re upgrading, review the changes in business requirements since the initial system was implemented.
In both situations, you need to set clear objectives. Define what issues you plan to solve with the introduction of the ERP. Try to identify measurable goals you plan to achieve.
Think about the expenses. ERP software prices differ based on the seller, modules required, cloud, on-premise, or hybrid setup, third-party implementation, etc. Higher costs don’t always mean a better system. If you pay more for features you won’t use, it’s not worth it. That’s why assessing your needs and shaping your financial policy is crucial when starting with ERP.
Create a practical ERP implementation plan. ERP software has many features affecting various parts of your business, so plan carefully. There are no identical solutions on the market. Some of them can easily adjust to business processes, the others need a greater deal of effort to work properly. Careful analysis may help you make the best choice and ensure a quick and trouble-free launch of the new system. Make this plan before picking software to know the costs and resources needed for success.
Did you start your journey to choose the variant that will help your company prosper and grow? This article will help you not to lose yourself in a variety of offers. Consider our Top 20 solutions and pick the best that satisfies your needs.
Discover the game-changing technologies that are reshaping the whole business management system, and gain insights into how ERPs can elevate ventures to new heights.
ERP Integration
Now, we’ll examine why it’s so important to properly integrate an ERP system, along with its pros and cons.
What Is ERP Integration
ERP integration is the way the ERP system is connected with other software. It is the key to achieving the need for seamless data management allowing business owners and managers to connect their ERP solution with various applications. The main goal of integration is to provide precise and synchronized data exchange for the correct performance of the business functions.
Integration acts like a connecting link between the ERP and other systems and helps businesses use information from various origins to make well-informed choices. It improves the transparency and productivity of each business process.
The Importance of ERP Integration
ERP Integration plays an important role in every business process because it broadens the possibilities of the ERP system and enables managers to use data more efficiently for better insights and decisions. Integration simplifies processes, maintains data accuracy, and assists organizations in adapting to tech changes and staying competitive. The more data is inputted into the ERP system, the better the result. So, it’s advisable to refrain from isolating other systems from the ERP.
The Key Benefits and Drawbacks of ERP Integration
ERP integration involves merging previously isolated systems to create a unified and reliable source of information. It helps to streamline business processes and improve efficiency. But, like anything else in this world, ERP integration has its disadvantages.
Check this table to learn more:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|
✅ Enhanced Business Processes One can get a broader view of the processes because a single source of information gives better pictures than numerous unrelated systems. |
❌ Restricted Visibility Monitoring and managing software integration projects that involve multiple systems and teams can pose significant challenges. Keeping track of progress and resolving issues becomes complicated and hinders the overall success of the project. |
|
✅ Upgraded Inventory Management Activities ERP integration gives access to up-to-date comprehensive data on stock, supply chains, business partner relations statuses, etc. It helps track materials and goods and ensures accurate order processing and timely manufacturing. |
❌ Systems with Incompatible Data Data incompatibility can be a big headache during software integration projects. When one works with systems separately, it’s not a problem because they don’t interact. However, in the process of software integration, issues with data structure, format, and meaning can arise. It often requires significant efforts to convert and transform the data. |
|
✅ Improved Relationship between Departments ERP integration makes departments work better together. It enhances the visibility and lets them collect and share data easily. This helps everyone have the latest information and adjust current goals. Departments can swiftly exchange their ideas and check the necessary data without mistakes and misunderstandings. Efficient teamwork inspires innovation and development and motivates employees to achieve common goals. |
❌ Internal Resistance to Implementation of New Software It’s very hard to maintain a competitive edge without using modern business software. Unfortunately, sometimes software project teams spend lots of time dealing with employees who resist the new system. One should be prepared for the fact that giving employees a new software system can cause some discomfort and resistance. |
|
✅ Boosted Customer Satisfaction The one and only source of information helps businesses arrange the data about the counterparties and choose the best strategy for meeting customer requests deeper. |
❌ Absolute Success Is Not Guaranteed Any kind of integration can’t guarantee a company’s fast and ultimate success. There are still a lot of factors that influence business development besides the software. |
ERP Pricing
The cost of ERP systems can vary dramatically depending on different factors:
-
Cloud ERP systems are initially cheaper than on-premise software. The client does not need to buy additional equipment, they only need to pay for using the ERP according to the chosen plan. The supplier is responsible for maintaining and updating the entire system.
Examples: Kladana offers a free plan for one user and one company. The Start plan, which includes basic inventory management features, is available for $60 per year. For a comprehensive ERP solution with a manufacturing module, ten users, and nearly unlimited access to all features, the price is $1,080 per year. Additionally, there are two intermediate plans available.
-
On-premise solutions are initially more expensive than cloud-based ERPs, but the client pays for their use only once. The supplier will not charge recurring fees for his product. Also, the payment for local software should include the cost of equipment and its maintenance, payment for web servers, and hiring new employees to keep the system working.
Examples: Microsoft Dynamics 365 (from $73 per user/monthly for basic configuration, from $68 per user/monthly for each of the basic modules).
-
A hybrid model may cost more than the two above-mentioned variants since it requires paying regular fees for its cloud components and needs funds to maintain its on-premise units.
Examples: TallyPrime (from $630 per user/annually).
-
Prices for ERP also vary depending on the functions and capabilities. The basic configuration of the solution usually includes the main modules for managing production, inventory, and orders. Additional features connection requires payment above the basic plan.
Examples: Tranzact (from a free plan for basic configuration to $4,300/annually).
ERP Vendors
While selecting the best ERP for your company, you may get concerned about the features, the complications of the launching, hidden costs, possible warning signs, etc.
Plus, you might get overwhelmed by the multitude of ERP software options. The market meets high demand with plenty of ERP solutions and their vendors. ERP vendors are companies that not only make and sell the software. They also update and improve their products to match their clients’ changing preferences.
In the next paragraph, we will give examples of the best ERP vendors and solutions. We talk about well-known names like SAP, Oracle, and Microsoft, along with some not-so-popular companies.
ERP Examples
| Software Name | Brief Description | Rating |
Kladana |
Cloud ERP system created for small and medium businesses. It helps business owners go digital and automate their inventory, production, and sales. It is used by D2C companies, manufacturers, wholesalers, retailers, and distributors. |
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
SAP ERPs |
One of the leading ERPs on the market. On-premise & cloud solutions for small businesses, a cloud solution for enterprises. Includes financial, inventory, purchasing, CRM, production, analytics, and other modules. |
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
DataNote (SAFAL) |
India-based both on-premise and cloud solutions for small and medium-sized businesses. Offers modules tailored for use in different industries. |
⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
Oracle NetSuite |
Cloud solution that performs many functions like managing inventory, manufacturing, accounting, warehousing, and supplies. |
⭐⭐⭐ |
Zoho One |
Zoho is a multipurpose software with a long history that has sales, marketing, HR, finance, and inventory modules. Also, can offer clients more modules like workspace, contact center, project management, and legal module. |
⭐⭐⭐ |
Microsoft Dynamics |
Modular prebuilt application designed by a famous brand. |
⭐⭐ |
TallyPrime |
A hybrid invoicing and accounting solution for SMBs with ERP features. |
⭐⭐ |
If you doubt your choice, sign up for a demo and see how Kladana can help solve your specific problems.
Key Takeaways: Understanding ERP Solutions
- ERP system is a multifunctional software that helps organizations manage and improve their processes.
- A common database and modules that can interact with each other are the core elements of any ERP system. Information entered by one user is available to everybody in the company. This helps employees stay informed, make better decisions, and adapt to changing conditions.
- ERP system is a multifunctional software that helps organizations manage and improve their processes.
- ERP solutions include several different software modules. Each of them focuses on different aspects of business. Common modules cover tasks like inventory management, product planning, procurement, sales, finance, marketing, and human resources.
- ERP solutions include several different software modules. Each of them focuses on different aspects of business. Common modules cover tasks like inventory management, product planning, procurement, sales, finance, marketing, and human resources.
- ERP solutions can be ranged according to the method of deployment, including on-premise implementation, public and private cloud hosting, and various hybrid setups.
- ERP solutions are gaining popularity among businesses representing every industry. To meet growing demand EPRs discover more and more features satisfying clients’ needs.
- ERP vendors offer dozens of solutions created to meet different requirements. You shouldn’t hurry to accept the most well-known brand. It’s better to think carefully, choose several ERPs, and check their features carefully.
Frequently Asked Questions on ERP Systems
Now, let’s take a closer look at common questions you might have about ERP solutions.
What is an ERP system in simple terms?
An ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) system is a software platform that helps organizations manage and integrate important parts of their businesses, such as supply chain, operations, reporting, manufacturing, and human resource activities, all in one place.
What is an example of an ERP system?
Kladana, SAP ERPs, DataNote (SAFAL), Oracle NetSuite, Zoho One, Microsoft Dynamics, TallyPrime, etc.
What are the 3 common types of ERP?
- Cloud‑based ERP: Hosted on the vendor’s servers and accessed through the web;
- On‑premise ERP: Installed locally on a company’s own computers and servers;
- Hybrid ERP: Combines elements of both cloud and on‑premise solutions.
What are the 5 components of ERP?
- Inventory Management: Tracks stock levels and manages supply chain operations;
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Manages customer interactions and sales;
- MRP: Manages BOMs, production orders, reports & raw materials supply;
- Finance: Supports financial reporting, and payrolls;
- Order Management: Supports sales & purchase orders, and has integrations with Shopify and other popular solutions.
What are the benefits of ERP for SMEs?
For SMEs, ERP systems can significantly enhance efficiency by automating routine tasks, improving data accuracy, offering real‑time business insights, and facilitating better decision‑making. They also help in scaling operations and improving customer service by ensuring that all departments are aligned and work more cohesively.
What is the future of ERP systems?
The future of ERP systems is moving towards more flexible, cloud-based platforms that offer advanced analytics, artificial intelligence capabilities, and improved user experiences. Integration with IoT (Internet of Things) devices and mobile accessibility are also becoming standard features, allowing businesses to be more connected and responsive to their operational needs.


