Barcoding in a warehouse enables tagging each warehouse unit, including products, product packaging, work‑in‑progress (WIP), containers, boxes, racks, forklifts, and other equipment. This allows warehouse workers to track stock movement of the entire warehouse inventory. Simply put, it brings order and improves efficiency.
In this article, you’ll find some surprising data: 48% of respondents in a survey conducted by riteSOFT claimed that less than 10% of their inventory is barcoded. Eventually, businesses lose money. But don’t worry — we’ve got you covered: we’ve described a warehouse barcoding implementation step‑by‑step scheme, examined typical pitfalls and challenges, and observed recent trends such as barcode-scanning drones and wearable barcode-scanning devices.
- Are Barcodes Still Used in Logistics? 3 Warehouse Barcoding Benefits
- Recent Warehouse Barcoding Trends
- Is it Difficult to Implement a Barcoding System in a Warehouse? Six Steps to Take
- What Are the Challenges You Can Face While Implementing Barcoding in Your Warehouse? Four Typicals Problems and Ways to Overcome them
- What Are the Best Practices for Maintaining Your Barcoding System?
- Frequently Asked Questions on Barcoding in a Warehouse
Are Barcodes Still Used in Logistics? 3 Warehouse Barcoding Benefits
Labeling products in a warehouse is not just a contemporary practice. It’s essential for keeping a warehouse in order. However, not all entrepreneurs can find time and spend effort to label all their products stored at multiple locations. For instance, riteSOFT claims that 48% of their survey respondents said that less than 10% of their entire inventory was barcoded. Later we’ll examine the consequences this can lead to.
There is a wide variety of barcoding types, commonly categorized as 1D and 2D barcodes. Detailed information on barcode types and hardware used for barcoding can be found in the article “Barcode Inventory Solutions 2025: Top 12 Software Tools for Managing your Business”.
Now, we’ll delve into the benefits of warehouse barcoding.
Accuracy and Efficiency
According to Stitch Labs poll, 62% of respondents named human errors the leading cause of warehousing issues. Manual data cannot provide 100% accuracy. Even the most diligent make mistakes if they are tired or distracted. Human labour should be better used for processing and analyzing data rather than monotonous tasks.
Additionally, no human being inputting information by hand in a notebook or filling in a spreadsheet can compete in speed with barcoding systems and machines.
🧊 4 Free Inventory Ckecklists
Learn how to manage stock, set up your warehouse, track barcodes, and build product cards for e‑commerce — even if you’ve never done it before
✅ Inventory management
✅ Warehouse setup
✅ Barcode tracking
✅ E-commerce product cards
Real‑Time Tracking and Monitoring
A manager or business owner can control stock at any time: how many goods are on hand, committed, or awaited. Without it, typical problems like stock shrinkage or overstocking — which became more common after the COVID‑19 crisis — occur. We seriously doubt that there is a businessman who wishes their warehouse to contain boxes randomly piled up:
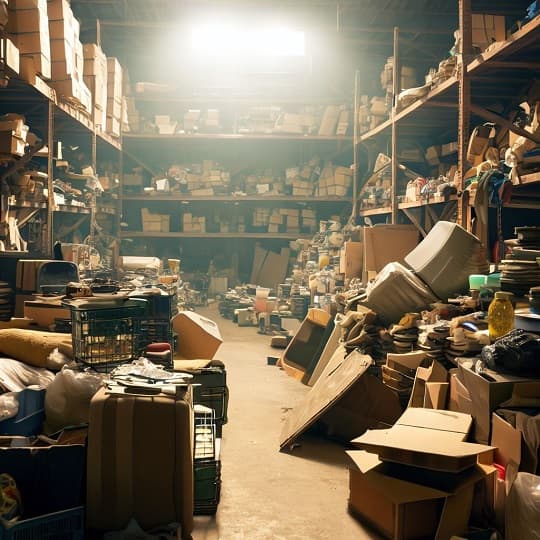

All in all, warehouse barcoding significantly improves inventory control.
Cost Savings
The long‑term financial benefits of implementing a barcode system in a warehouse are evident. Multiple errors lead to product write‑offs, termination of counterparty agreements, frequent employee fines, and dismissals. Eventually, a business loses money.
Read‑alikes
Barcode Inventory Solutions 2025: Top 12 Software Tools for Managing your Business
Inventory Management in Excel: Free Template and a Step‑by‑Step Guide
Inventory Management Guide for Beginners: Techniques, Challenges, Best Practices, and Trends
Inventory Counting: Step‑by‑Step Guide on How to Conduct and Access the Results
Recent Warehouse Barcoding Trends
One of the most modern and widely-spread warehouse technologies is barcode-scanning drones. These drones autonomously fly according to a set path in a warehouse and scan barcodes via built‑in cameras. Alternatively, drones can be controlled by an operator. All the scanned data is accessible in a warehouse management system (WMS) and can be processed by managers.
The benefits of barcode-scanning drones are the following:
- Speeding up all warehouse operations compared to traditional manual barcode-scanning
- Eliminating human errors
- The ability to scan products in large warehouses where some storage bins can only be accessed using specific equipment such as forklifts
- Reduced risk of worker injuries compared to using forklifts
- No need to interrupt basic operations such as sales and merchandising for manual stock-takes
Wearable barcode-scanning devices are another emerging trend. Usually, these devices are shaped like wristbands or even finger gadgets, making them more convenient compared to heavier barcode scanners.

RFID and AI are among other long‑term warehouse barcoding trends.
Is it Difficult to Implement a Barcoding System in a Warehouse? Six Steps to Take
Implementing barcoding in a warehouse may seem straightforward, but it can be tricky. Let’s examine the typical steps and explore potential pitfalls.
Step 1. Initial Assessment
Don’t rush to implement any barcoding system in your warehouse. You will unlikely reach your goals and get disappointed with barcodes. We recommend assessing your current conditions. Answer the following questions:
- How do you currently label your inventory in the warehouse?
- Do you analyze the results? Are you satisfied with them?
- Have you tried different labeling methods before? Why did you abandon them?
- What goals do you want to achieve with warehouse barcoding?
- How many types of warehouse units do you have that need barcoding?
- How many warehouse units do you have in total, approximately?
- What budget do you have for barcoding hardware (scanners, printers, drones) and software?
- Can you allocate time for switching to a new system and employee training?
- What barcode types will you use?
While answering these questions, you’ll probably undercover some more. That’s fine. No rush needed, take your time.
Step 2. Make up a Warehouse Barcoding Plan
Start by revising your current warehouse layout, including rack layout, transit routes, shelving, and bin storage. How will the new system influence the way your warehouse operates now? Define a detailed, staged plan with duration and assignees. Be flexible to make changes as needed.
Step 3. Choose the Right Hardware
Compare options for scanners, printers, mobile devices, and drones in a spreadsheet. Don’t spend too much money on all existing and trending devices. Start with the basics and upgrade hardware gradually if needed.
Step 4. Design Barcode Labels
Keep your product labels simple: use a readable font and a large font size, don’t forget to emphasize units of measurement (UOMs) and quantity, discounts, expiry dates, and other important details. In case you have a branding design system, use your logo and brand colours.
As to labeling boxes, palettes, racks, and other warehouse units, you’ll need a certain label system. Segment labels according to an item type, storage location, or priority level. For example, red labels for boxes with perishable goods, green labels for single items, and blue labels for bundles. This is just a random example, you’ll need to craft a colour-coding system which will be convenient for you to use. Such a colour scheme has to coincide with your WMS and the logic of your layout.

Create Your Labels with Your Unique Design in Kladana
In Kladana, you can generate and autogenerate GTIN, EAN‑13, EAN‑8, Code‑128 & UPC barcodes for your products, bundles, and packaging. Print thermal labels and price tags in bulk. Also, you can get your tailor-made labels, adding a product’s weight, picture, serial number, washing mode icons, and more.
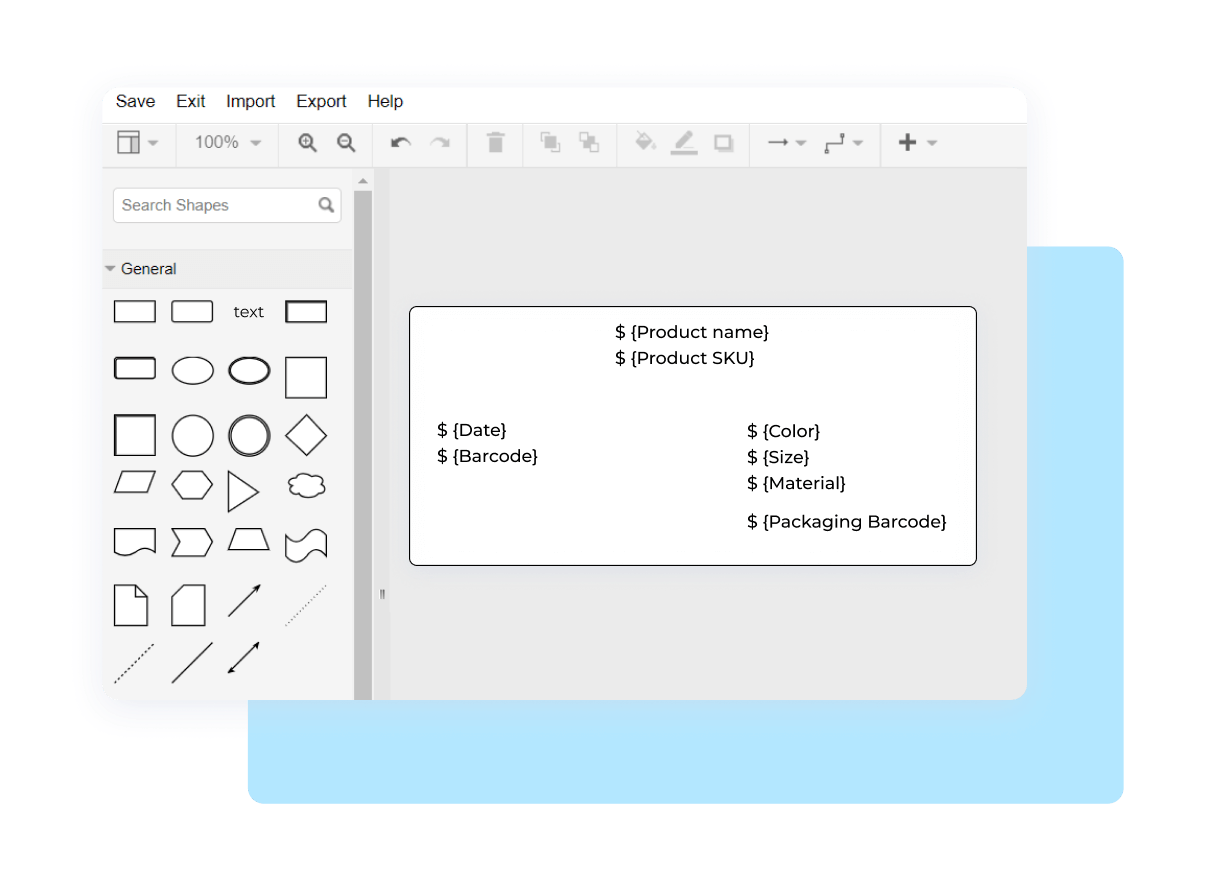
Step 5. Software Integration
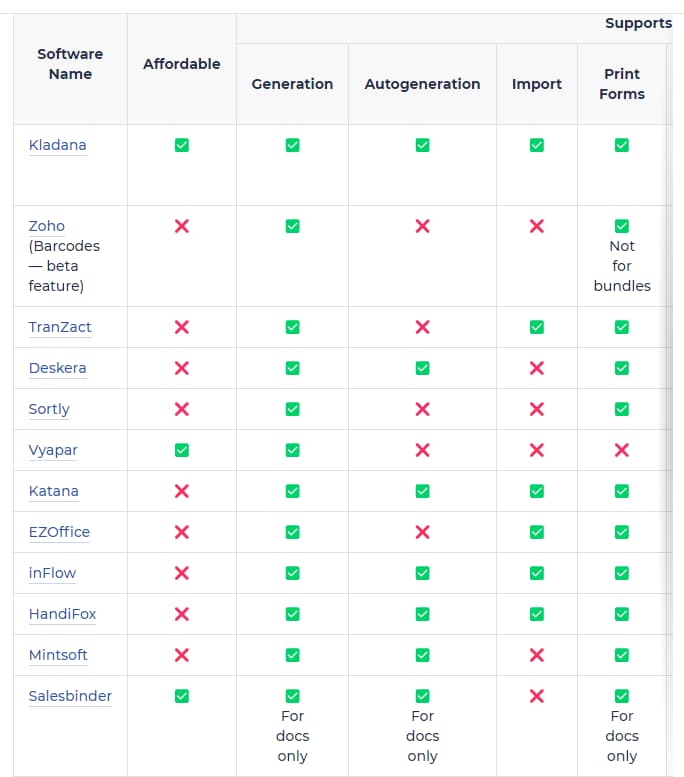
Integrate barcoding with your existing or new warehouse management system (WMS). Integrate barcoding with your existing or new warehouse management system (WMS). Consider top-rated barcode inventory software and essential criteria for selection.
ERP for $60 a Year
Manage inventory, warehousing, production, and sales in one app.
Step 6. Training and Development
Ensure your staff is well-trained on the new warehouse barcoding system. Assess the initial results of your new system and make changes if necessary. Lastly, don’t avoid ongoing inspection of the entire warehouse barcoding system.
What Are the Challenges You Can Face While Implementing Barcoding in Your Warehouse? Four Typicals Problems and Ways to Overcome them
Hardware malfunction and maintenance issues may prevent you from keeping your barcoding system running smoothly. While choosing hardware, pay attention to the service conditions provided by the equipment manufacturer — whether they offer regular maintenance and urgent repairs, what the terms are, how quickly it can be done, how many inquiries you have within a year. Manufacturers with a user-friendly approach usually offer quite costly hardware. However, they can save you from long‑term operational downtime.
Software bugs and mistakes happen rarely in comparison to manual labour. However, they are plausible. The same piece of advice here — we recommend opting for software developers who provide free and quick support. We don’t want to boast, but Kladana doesn’t charge you for support, doesn’t limit you to the number of inquiries and the support team responds within 5–15 minutes.
Also we recommend using cloud solutions. In case of bugs and critical error your vital data won’t be lost for good. Lastly, pay attention to robust security protocols to ensure that your data is protected and can’t be stolen.
Wrong hardware and software use by employees is an outcome of insufficient staff training. It’s tremendously important to make sure that an employee holds a barcode scanner at a proper distance, for example. Or that an employee knows how to utilize particular software features. Supervising managers should ensure correct usage to avoid human errors.
Barcodes get mixed up and duplicated during some warehousing operations. For instance, during receiving you scan a supplier’s barcode but then a barcode will be autogenerated in your wms. Later, while conducting inventory counting, or shipment, you’ll have two barcodes of one item. To avoid this, you’ll have to create a strict barcoding plan. Also, if the layout and colour schemes are not set properly, products will appear in wrong storage bins, and customers will get wrong orders.
What Are the Best Practices for Maintaining Your Barcoding System?
Conduct regular inventory audits according to your layout and barcoding plan. Focus on seasonal and perishable goods to prevent selling damaged products and avoid overstocking. Make stock adjustments, sales, and write‑offs in case of any discrepancies. For instance, Christmas decorations can be better sold with a 70% discount in spring in order to free storage space for other products in demand.
Read our full guide on inventory counting
Conduct ongoing employee training and run tests: it’s not enough to show your employees once how to perform barcoding tasks. You’ll have to revise the barcoding procedure from time to time, especially when any changes take place. Conduct tests to ensure proper understanding and implementation.
Upgrade warehouse barcoding equipment and purchase supplies on time: one outdated or malfunctioning barcode scanner can lead to numerous mistakes. Say, an employee makes 400 scans per working day. These are 400 crucial errors that will lead to money loss even if you identify the problem soon. If an ink cartridge for a printer gets empty, your employees won’t be able to print barcodes for a while. As a result, all the warehousing operations will be disrupted.
Frequently Asked Questions on Barcoding in a Warehouse
While contemplating the use of barcodes in a warehouse, you may have a couple of questions. Let’s find some answers.
What is a barcode and how does it work in a warehouse setting?
A barcode is a machine-readable code consisting of numbers and a pattern of parallel lines. In a warehouse, barcodes are used to identify and track items (products, palettes, equipment) quickly and accurately. When scanned, the barcode reader translates the pattern into data that can be used for inventory management.
Why is barcoding important for warehouse management?
Barcoding enhances accuracy, speed, and efficiency in warehouse operations. It reduces human errors in data entry, improves inventory tracking, and speeds up the processes of receiving, picking, packing, and shipping.
How does barcoding improve inventory accuracy?
Barcoding minimizes manual entry errors by automating data capture. Each scan instantly updates the inventory system with precise information about the item, including its location and quantity, leading to more accurate inventory counts and stock levels.
How do I implement a barcode system in my warehouse?
To implement a barcode system, follow these steps:
- Select the right barcode software and hardware (scanners, printers).
- Create barcode labels for all inventory items.
- Integrate the barcode system with your WMS.
- Train your staff on how to use the barcode scanners and software.
- Regularly maintain and update the system to ensure it runs smoothly.
Can barcoding be integrated with existing warehouse management systems (WMS)?
Yes, barcoding can be integrated with most WMS software. This integration allows for real-time updates and seamless data flow between the barcode scanning devices and the WMS, enhancing overall operational efficiency.
What is the difference between 1D and 2D barcodes?
- 1D barcodes: Linear and consist of a single row of bars and spaces. They are used for simpler applications with less data.
- 2D barcodes: Include QR codes and are capable of holding much more information, including URLs and detailed product data, in a smaller space.
What types of barcodes are commonly used in warehouses?
The most common types of barcodes used in warehouses are:
- UPC (Universal Product Code): Typically used for retail products.
- Code 39 and Code 128: Often used for various logistics and inventory purposes.
- QR codes: Used for storing more complex information and quick scanning.
What are the costs associated with implementing a barcode system?
Costs can vary depending on the size of the warehouse and the complexity of the system. Generally, expenses include purchasing barcode printers, scanners, software, and labels, as well as training staff and ongoing maintenance.
How do barcodes help with warehouse space optimization?
Barcodes streamline inventory tracking, making it easier to locate items quickly. This efficiency can lead to better space utilization, as items can be stored and retrieved more effectively, reducing wasted space and improving overall warehouse layout.
How to use a colour-coding barcode system in a warehouse layout?
Colour-coding barcodes can enhance the organization and efficiency of a warehouse. Assign different colours to barcodes based on categories such as item type, storage location, or priority level. This visual differentiation helps warehouse staff quickly identify and locate items, streamline sorting and picking processes, and reduce errors. Ensure that the colour-coded system is consistently applied and that staff are trained to understand and use the color codes effectively.
What are the common challenges in implementing a barcode system, and how can they be overcome?
Common challenges include:
- Initial setup costs: start with a basic system and scale up as needed.
- Staff training: provide comprehensive training sessions.
- System integration: work with IT professionals to ensure smooth integration with existing systems.
- Barcode durability: use high-quality labels and printers to ensure barcodes withstand warehouse conditions.
Can barcodes be used for tracking perishable goods?
Yes, barcodes can be used to track perishable goods by including information such as batch numbers and expiry dates. This ensures that stock is rotated properly and reduces the risk of selling expired products.
How do barcodes assist with order fulfillment?
Barcodes speed up the picking process by allowing workers to quickly scan items to verify order accuracy. This reduces the likelihood of errors and ensures that customers receive the correct products promptly.
How can barcoding technology evolve in the future and what are the current trends?
Advancements in barcoding technology may include:
- Barcode-scanning drones.
- Barcode-scanning wearable devices.
- Integration with IoT (Internet of Things): for real-time tracking and smart warehousing.
- Advanced data analytics: to gain deeper insights into inventory trends and warehouse efficiency.
- Mobile scanning solutions: enhanced capabilities for smartphones and tablets to be used as barcode scanners.
What are the best practices for maintaining a barcode system in a warehouse?
- Regularly update and maintain your barcode software.
- Ensure all barcode scanners and printers are in good working condition.
- Perform routine checks to verify barcode readability.
- Keep your inventory data up‑to‑date and conduct periodic audits.


