Stock-taking may seem like a routine task, but businesses that skip it or perform it irregularly often suffer financial losses and operational inefficiencies. Here’s how poor or infrequent stock-taking can lead to negative outcomes.
Imagine you own a retail store. Without regular stock-taking:
1️⃣ You assume you have 50 best-selling items in stock, but in reality, only 10 remain. Customers leave disappointed, and you lose sales.
2️⃣ You order more of a slow-moving product, thinking it sells well. Instead, it sits in storage, taking up space and increasing holding costs.
3️⃣ An unnoticed theft or data entry error results in thousands in losses before the issue is detected.
At the end of this guide, you’ll find a stock-taking checklist to streamline your inventory counting procedures and improve accuracy.
- What is Inventory Counting?
- Why is Regular Stock-Taking Essential?
- Preparing for Inventory-Taking
- Assets Checked during Stock Counting
- Types and Techniques of Stock-Taking
- Inventory Cycle Counting for Ongoing Accuracy
- The List of Employees Financially Liable for Stock-Taking
- Stock-Taking in 2025: Step‑by‑Step Guide
- Best Practices for an Efficient Stock-Taking Processes
- Common Inventory Discrepancies and How to Resolve Them
- How to Consider the Human Factor in Inventory Count Procedures
- Automated Stock-Taking for Faster and More Accurate Results
- Stock-Taking Checklist
- Frequently Asked Questions on Stock-Taking
What is Inventory Counting?
Inventory counting, also known as inventory-taking, is the process of physically verifying and recording the quantity of goods and materials a business holds. It helps identify discrepancies between recorded and actual stock levels, ensuring accurate financial and operational data.
The primary goal of the inventory counting process is to detect stock shortages, prevent overstocking, and improve overall warehouse management. To minimize sales disruptions, many businesses schedule regular inventory count procedures after working hours or on designated days.
📊 Start managing inventory like a pro — even if you’re just getting started
🧊 4 Free Inventory Ckecklists
Learn how to manage stock, set up your warehouse, track barcodes, and build product cards for e‑commerce — even if you’ve never done it before
✅ Inventory management
✅ Warehouse setup
✅ Barcode tracking
✅ E-commerce product cards
Why is Regular Stock-Taking Essential?
Accurate inventory count procedures help businesses:
✔ Prevent stockouts, ensuring customers always find what they need.
✔ Avoid overstocking, which ties up capital and raises storage costs.
✔ Reduce dead stock, minimizing waste and unnecessary write-offs.
✔ Detect theft and fraud, ensuring accountability in your supply chain.
✔ Improve financial planning, with real-time data on available stock.
Preparing for Inventory-Taking
Conducting an inventory count requires time, workforce, and planning. Key considerations include:
- Assigning roles to employees (e.g., inventory counters, supervisors)
- Allocating overtime pay for extended work hours
- Managing potential revenue loss during stock verification
For single-person businesses, inventory counting means handling multiple tasks, including stock verification and financial reconciliation. A well-structured inventory-taking process reduces errors and improves efficiency.
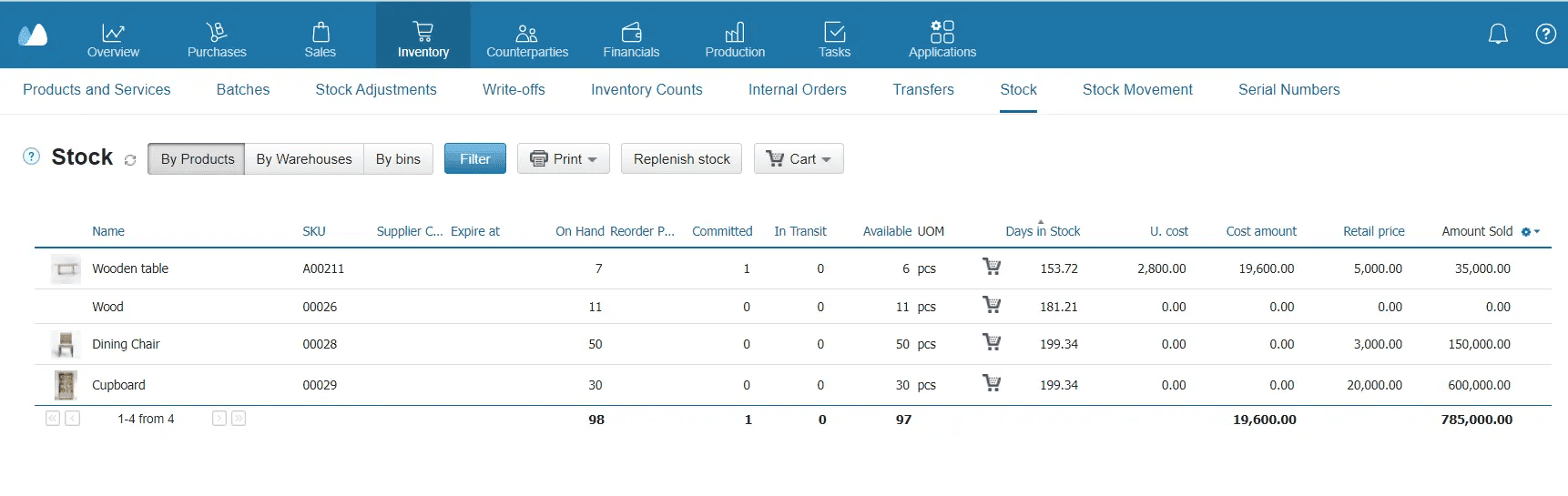
Assets Checked during Stock‑Counting
There are several categories of things subject for inventory counting:
- Raw materials;
- Finished goods;
- WIP (work‑in‑progress);
- Equipment;
- Tools, spare parts, and cleaning supplies.
As material, as intangible assets can be checked.
Types and Techniques of Stock-Taking
The right inventory counting method depends on your business needs and goals. Here are the key classifications:
| Type | Meaning |
By Situation |
|
Scheduled Counting |
Planned stock-taking conducted on a fixed schedule, approved at the start of the fiscal year. Employees are notified in advance. |
Unscheduled Counting |
Performed after incidents like theft, natural disasters, or management changes. |
Repeated Counting |
Used when initial audit results are disputed or errors are suspected. |
Control Counting |
Conducted after regular stock-taking to verify accuracy. |
By Scope |
|
Full Inventory Count |
Involves auditing all assets across the business. |
Partial Inventory Count |
Focuses on specific departments, categories, or product lines. |
By Method of Conduct |
|
Physical Inventory-Taking |
Physically verifying stock levels against records. |
Documentary Inventory-Taking |
Cross-checking inventory records, invoices, and purchase orders without a physical count. |
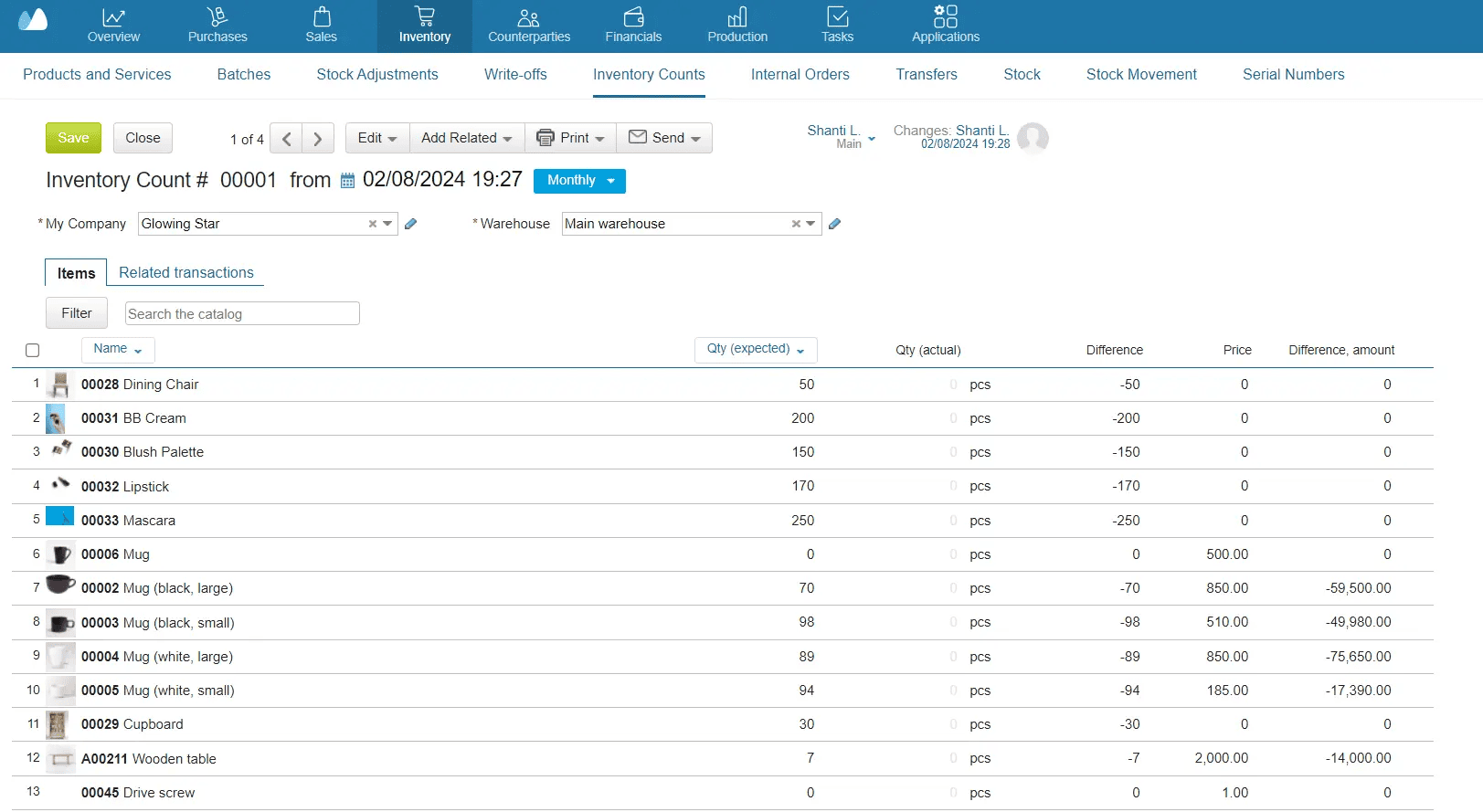
Inventory Cycle Counting for Ongoing Accuracy
As a rule, in a store and warehouse, the inventory counting is conducted every month — to control the work of the staff and the overall state of the assets. If you apply such a control mechanism, you can assess the quality of employees’ work, timely identify scrap, and remove from the product range those items that, for some reason, do not sell.
The head of the organization determine:
- The number and dates of stock-takings in the fiscal year;
- The list of property to be checked;
- Financial obligations for each check.
Common Cycle Counting Methods
Some businesses use inventory cycle counting. It’s one of the best inventory practices when a small amount of inventory is regularly checked at a specific time. For instance, a sports equipment shop checks the stock of dumbbells every Tuesday, and fitness balls — every Wednesday, once a fortnight. The advantage of this approach is that it doesn’t require as much effort as formal stock-taking and can help identify discrepancies promptly. Stock cycle counting can be of different types and techniques.
ABC Cycle Counting
All goods are divided into three categories in which particular inventory counting rules are determined.
- A-items: High-demand products, counted weekly to prevent stockouts. (Example: Popular shoes in a fashion store.)
- B-items: Moderate-demand items, counted monthly. (Example: Office supplies.)
- C-items: Low-demand stock, counted quarterly. (Example: Seasonal decorations.)
Not only demand can be a decisive factor for classification but also storage space in a warehouse, price, etc.
Random Sample Counting
Ideal for businesses with large numbers of similar items (e.g., screws, beads, electronic parts). Example: A jewelry store randomly counting gold chains.
Control Group Cycle Counting
Focuses on a specific set of products repeatedly to find procedural flaws. Example: A warehouse double-checking electronic devices prone to returns.
Opportunity-Based Counting
Stock-taking occurs when items reach reorder points or are transferred between locations. Example: A supermarket checking dairy products before restocking.
The List of Employees Financially Liable for Stock-Taking
Certain employees are accountable for inventory accuracy:
- Warehouse keepers & Store Managers — Oversee stock movement and ensure records are updated.
- Sales & Cashiers — Must report discrepancies at the point of sale.
- Inventory Auditors & Accountants — Handle stock adjustments and reconciliation.
This condition is stipulated in the employment contract. Financially liable employees participate in the checks of the values for which they are responsible for safekeeping.
Stock-Taking in 2025: Step‑by‑Step Guide
Stock-taking in a store and warehouse essentially involves counting and assessing the availability of goods. If any problems with the quality or quantity occur, the corresponding inventory counting documents must be made, and then related operations should be conducted such as write-offs and stock adjustments. This is usually followed by the decision to recover damages from financially liable employees. However, it depends on the inner policy of a company.
The process can be quite complex, especially for beginners, so we have developed a table that visually guides you on how to conduct inventory counting.
| Stage | Actions |
Preparation for inventory audit |
The director issues an order and creates a commission, including the financially liable employees, if available. If not, then only the director themselves, but in different functional roles. In some companies, an accountant can also take part in the procedure. |
Conducting stock-taking and recording its results |
The list of assets is printed, and the commission members count the available goods. Data is entered in the «Actual Availability» column. |
Reconciliation of the actual inventory result with inventory data |
A reconciliation statement is formed. Acts and other documents explaining discrepancies between actual and accounting data are filled out. |
Summarizing inventory counting results |
A decision is made to recover damages from the responsible parties if any. |
Let’s examine the stages indicated in the table in detail. Disclaimer: we are going to scrutinize the usual way of conducting stock audits. However, its stages can depend on a particular legislation of a country and the company’s inner rules.
Step 1: Preparation for Stock-Taking and Assembly of the Commission
Inventory counting in a store or warehouse usually begins when an order for stock-taking is issued, which must be signed by the manager or owner of the company.
Next, a special commission must be formed, which is composed of administrative and managerial staff. Sometimes representatives of the internal audit service and experts from independent auditing organizations are also included. Financially liable people, such as salespersons or warehouse workers, cannot be members of the commission but must be present during the inventory.
Let’s look at the requirements in more detail.
In trading organizations sometimes this process starts unexpectedly for salespeople and warehouse workers — employees don’t know anything until the commission arrives at the store or warehouse. After that, the sale and movement of goods subject to inventory are prohibited. That is, either the entire warehouse or store must be closed, or just the audited department and the cash register in the department.
Stock audits at the warehouse and the retail outlet differ in that counting goods in the warehouse is much more difficult than on the store shelves, so it takes more time and effort. To simplify the process in a large store, you can create an inventory audit plan, for example, according to the layout of the goods. In this case, after the inventory counting, you can directly record the actual quantity of products on it. This method is convenient for its clarity.
Step 2: Conducting the Inventory-Taking and Recording Its Results
During the inventory counting, the commission checks not only the quantity of goods but also their quality, storage conditions, and expiration dates. To record the results, a document on the actual availability of valuables is created, listing all goods by groups with the indication of an item name, SKU, UOM, its variants, serial numbers, batch numbers, and other characteristics that enhance the accuracy of inventory management.
Depending on the types of products presented in the shop and stored in the warehouse, procedures such as control weighing, measuring, and others are introduced in addition to counting.
If the stock management processes in your organization are automated, then the check is faster — stock data is printed from the software and compared with what is available on the shelves and in the warehouse.
This way, you can quickly detect shortages or excesses during the stock-taking. For this purpose, Kladana ERP is a convenient solution that will help maximize the speed of the check.
Step 3: Reconciling Actual Data with Inventory Records
Following the inventory check, the completed inventories are usually submitted to the accounting department. There, a reconciliation of the actual goods in stock with the data from the inventory management system will be conducted.
If there is no accounting department, the general director or the company owner substitutes the accountant.
Step 4: Summarizing Inventory Counting Results and Reflecting Them in Inventory Management System
At this stage, when there is a clear picture of the discrepancies, the manager issues an order to approve the results of the inventory. Based on this, it is possible to recover damages from the responsible parties and make the corresponding entries in the records.
Simultaneously, the accountant records all final figures and data regarding surpluses, shortages, waste, and sorting errors.
Best Practices for an Efficient Stock-Taking Processes
Establish a Clear Inventory Counting Schedule
- Decide on the frequency: daily, weekly, or quarterly.
- Assign responsibility to trained staff members.
Use Technology to Automate the Inventory Count Procedures
- Implement barcode scanners or RFID tracking for real-time stock updates.
- Use inventory management software like Kladana for automatic reconciliation.
Ensure Accurate Documentation
- Maintain clear records of counted items, shortages, and excess stock.
- Generate reports to analyze trends and improve future inventory-taking strategies.
Cross-Check with Sales and Purchasing Data
- Compare stock levels with purchase orders and sales records to identify inconsistencies.
Common Inventory Discrepancies and How to Resolve Them
Let’s examine four core reasons for inventory discrepancies and ways to resolve them.
Reasons for Inventory Discrepancies During Stock-Taking
As to the reasons discrepancies occur, there are a few most common:
Human error: incorrect data entry, miscounting, or misplaced items
Sometimes employees may lack knowledge, instructions, and training on how to manage inventory items — receive, store, transfer, and track. Let’s consider a couple of examples:
- An item has been returned but there are no records in the inventory system, and the product is considered to be sold;
- Products in a batch expired and were just thrown away without being correctly written off.
Outdated equipment & software: inaccurate records due to manual inventory-tracking
Malfunctioning or outdated tools & equipment (e.g. barcode scanners) may multiply errors. Inventory management in spreadsheets or paper notebooks can pile up these errors even more. The widely spread stock management mistakes are the following:
- Labeling items with wrong barcodes;
- Mixing up SKUs of different products;
- Storing goods in wrong locations and storage bins.
Theft & fraud: stock theft by employees or incorrect supplier deliveries
Warehouse staff can be involved in theft, as well as customers in a shop. Also, suppliers can use some fraud schemes.
Damaged goods: spoiled, broken, or lost inventory that isn’t properly recorded.
Resolving Inventory Discrepancies
Now, let’s move on and learn how to deal with inventory discrepancies.
Recount stock once again if possible.
If you get the same results, analyze the reasons why stock shortages or excess occurred. Check whether recent inventory operations were conducted correctly: receiving, storing, shipment, etc. Pay attention to products’ SKUs, barcodes, and variants.
During inventory counting, sorting errors are sometimes discovered — this is a simultaneous surplus and shortage of goods of the same name but of different variants. For example, according to the stock records, there are 6 boxes of Basmati rice and 4 of Jasmine rice in stock. However, during the inventory, it turns out that there are actually 3 Basmati and 7 Jasmine. This situation indicates a sorting error. In this case, it’s necessary to determine whether the goods are of equal price. In stock management, the amount by which the shortage exceeds the surplus is written off to financial results.
Make corresponding records in your inventory management system. Discrepancies identified during stock-taking, whether surpluses or shortages, need to be documented as income or expense.
Depending on the results of the analysis, resolve the issue. Sometimes, shortages during inventory counting are written off as customer theft or inventory management errors. Significant shortages for the organization are paid for by the person responsible for the material assets.
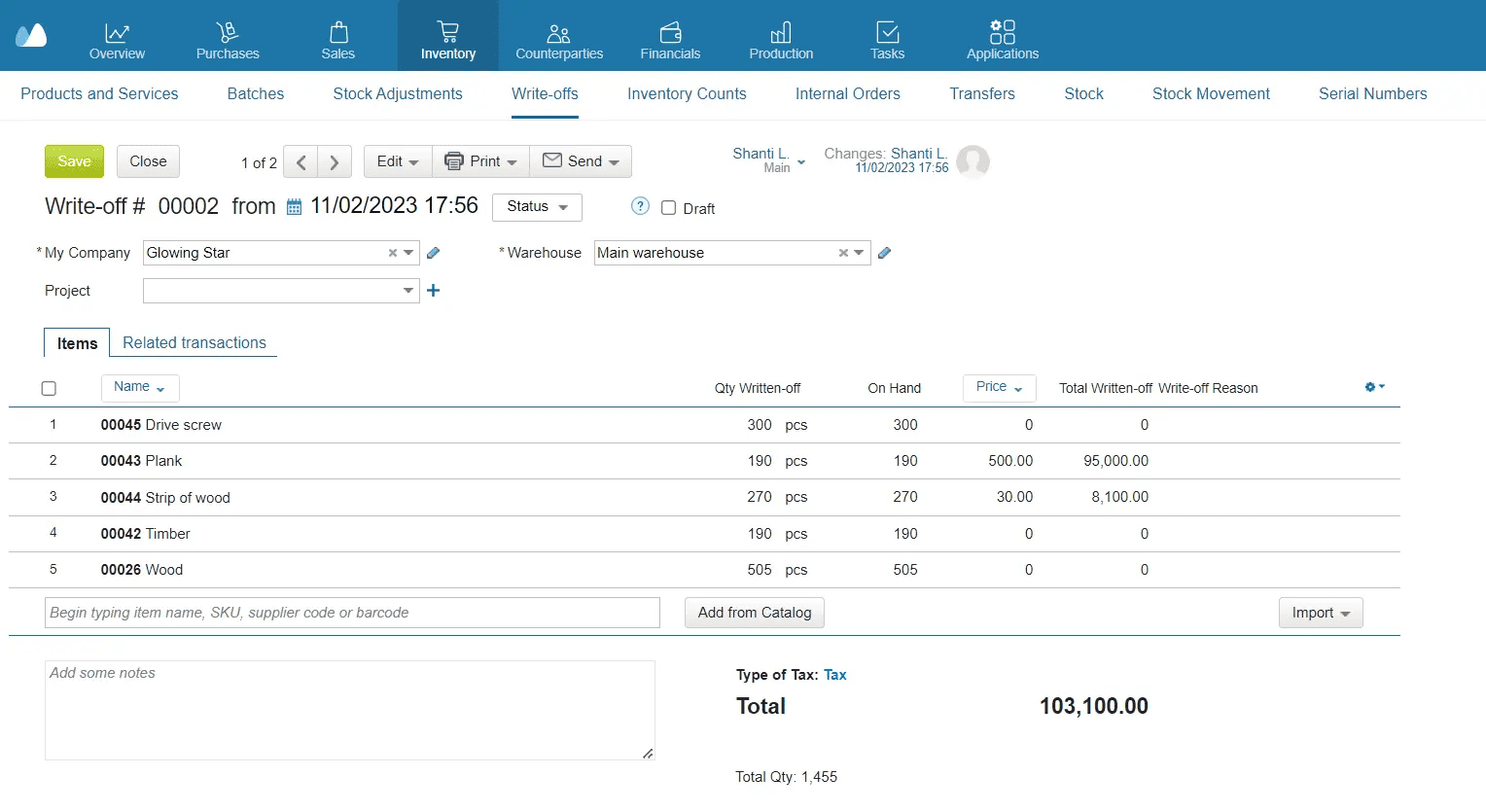
How to Reconcile Discrepancies
In most cases, employees responsible for shortages bear the liability — the missing sum can be deducted from their wages. However, the decision based on the results of the inspection is made by the management, and in practice, shortages are often written off as costs, especially if they do not exceed the established norms of the organization. Minor discrepancies are normal for any enterprise.
Surpluses can be attributed to the performance of the enterprise. In case of their occurrence, it is necessary to identify who is responsible, as surpluses also lead to discrepancies. Any results of the inspection — both positive and negative — are recorded in reports.
How to Consider the Human Factor in Inventory Count Procedures
Regular inventory auditing is necessary for the timely detection of employees’ dishonest actions and errors associated with the human factor.
Inventory mustn’t be just a formal event but a way to obtain information that reflects reality. To achieve this, it’s important to observe two conditions:
- Inventory should not increase the workload of the staff
If you assign a regular employee to conduct inventory counting, relieve them of their direct duties during this time. Alternatively, engage an external specialist to perform the check.
- The purpose of the inventory counting is to conduct accurate counts and summaries of the stock, not those that are favorable to the employees conducting the recount.
To avoid manipulations with goods and false information in documents, outsourcing services are a better choice. An employee who is not personally interested in the results of the inspection will not hide the real indicators and report false information.
What else to consider:
✔ Proper Training: Ensure staff understands inventory count procedures.
✔ Automated Solutions: Minimize manual errors with barcode scanners and stock‑taking software.
✔ Random Spot Checks: Surprise audits discourage theft and inaccuracies.
✔ Outsourcing Audits: Third-party inventory audits ensure impartial accuracy.
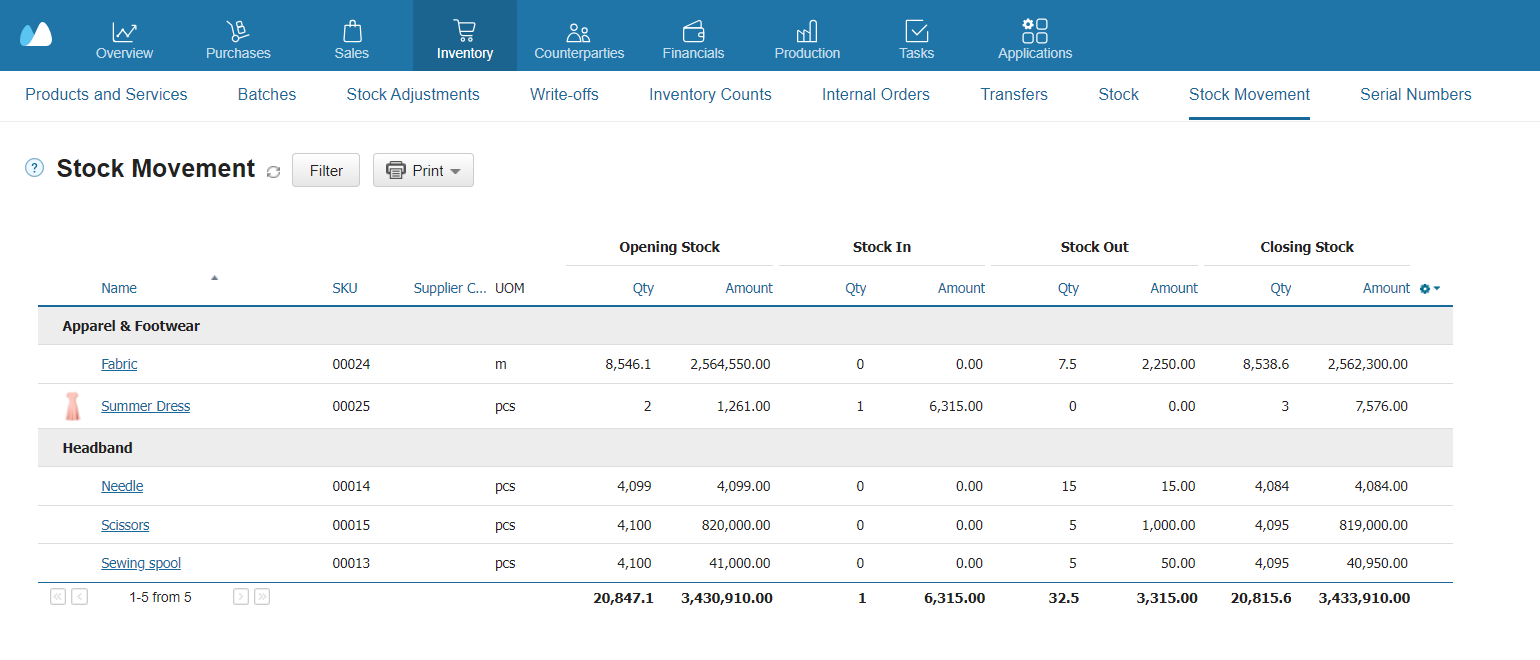
Automated Stock-Taking for Faster and More Accurate Results
Using an automated inventory counting system simplifies stock-taking and reduces errors. You always know how much stock should be in your store or warehouse. When you enter the actual data, you can quickly identify any shortages or excesses, both in terms of quantity and monetary value. However, closing a point of sale or department for inventory counting means temporarily halting sales, so it’s important to carry out the process as quickly as possible. This problem can be solved through automatic stock-taking.
To avoid errors leading to misplacement and excessive paperwork, you can automate the compilation process with Kladana. To do this, connect our software to a data collection terminal. You just need to scan the barcodes of products in the warehouse. The system automatically searches for discrepancies and then generates an inventory list. In Kladana, you can also download or fill out online all the documents needed for inventory counting: stock and stock movement reports, product cards, and others.
Inventory Doesn’t Have to Be a Mess
Start using Kladana to track stock accurately, reduce errors, and simplify audits — even during your trial.
Stock-Taking Checklist
To sum it up, let’s revise the learning material and create a handy stock-taking checklist:
✅ Choose a stock-taking method (cycle counting, full audit, etc.)
✅ Set up a stock-taking schedule
✅ Define inventory count procedures & documentation steps
✅ Assign responsible employees and ensure proper training
✅ Halt sales and warehouse operations during physical stock counts
✅ Conduct a thorough count and verify discrepancies
✅ Record findings in the inventory management system and take corrective action
✅ Continuously improve stock-taking efficiency based on past audits.
Frequently Asked Questions on Stock-Taking
Let’s explore the most common questions that novices often have when they are eager to conduct inventory counts.
What is stock-taking in simple terms?
Stock-taking is physically verifying inventory levels and comparing them to recorded data. Any discrepancies are corrected through stock adjustments.
What counts as inventory?
Inventory includes raw materials, work-in-progress goods, and finished products ready for sale.
What is cycle counting in inventory?
Cycle counting is a method of counting small portions of inventory at a time instead of conducting a full inventory audit all at once.
How often should stock-taking be done?
It depends on your business. High-volume retailers may need daily checks, while manufacturers may conduct monthly or quarterly counts.
How do you plan stock-taking?
- Schedule the count in advance.
- Train staff on stock-taking procedures.
- Organize inventory before counting.
- Use inventory software for accuracy.
How do you resolve stock discrepancies?
- Recount the stock to confirm the error.
- Investigate causes (theft, misplacement, or data errors).
- Update records and take preventive measures.
Should employees be fined for stock discrepancies?
Fining employees is discouraged, as errors often stem from systemic issues. Instead, focus on training and improving stock-taking processes.




