Piece rate pay, where employees earn compensation based on their output, is shown to enhance productivity and increase earnings:
✅ A study by the US National Bureau of Economic Research found that workers under piece rate systems earned, on average, 14% more than their counterparts on hourly wages.
✅ Furthermore, research in the agricultural sector by the University of California demonstrated that implementing piece rate pay reduced labor inputs significantly, with vineyard pruning requiring 19 man-hours per acre compared to 26 under hourly pay, without compromising work quality.
However, like everything in this world, piecework has not only advantages but also significant drawbacks:
❌ A Study showed that while this system can boost productivity, it may also lead to adverse health outcomes.
❌ According to the research by the International Labour Organization those paid by piece rate reported increased concerns about harassment, verbal abuse, and workplace accidents compared to hourly workers.
This article explores the mechanics of piece rate pay, its calculation methods, and the potential benefits and considerations for both employers and employees.
- What Is Piece Rate Pay?
- Types of Piece Rate Pay Structures
- How to Calculate Piece Rate Pay (With Examples)
- Pros and Cons of Piece Rate Pay
- Best Practices for Implementing a Piece Rate Pay System
- Frequently Asked Questions on Piece Rate Pay
- Conclusion — Is Piece Rate Pay Right for Your Business?
- Users Weigh In: Mixed Reactions to Piece Rate Pay
- List of Resources
What Is Piece Rate Pay?
Let’s disclose the essentials of the piece rate wage system.
Piece Rate Wage Definition
The piece-rate pay system is a method of calculating wages based on the amount of production output. The more tasks an employee completes or the more goods they produce, the higher their earnings.
Piece-rate pay is beneficial for those working in manufacturing, as it motivates them to produce as much as possible. However, an exception applies to high-precision industries, where the drive to increase output can lead to a rise in defects.
Difference between Piece Rate Pay, Hourly Wages, and Salary Pay
The piece rate pay method differs from hourly wages and salary pay in how earnings are calculated. With a piece rate wage system, workers are paid per unit produced or task completed. Their income depends on productivity. In contrast, hourly workers earn a fixed rate per hour worked, regardless of output. Salaried employees receive a predetermined amount per pay period, without direct link to performance.
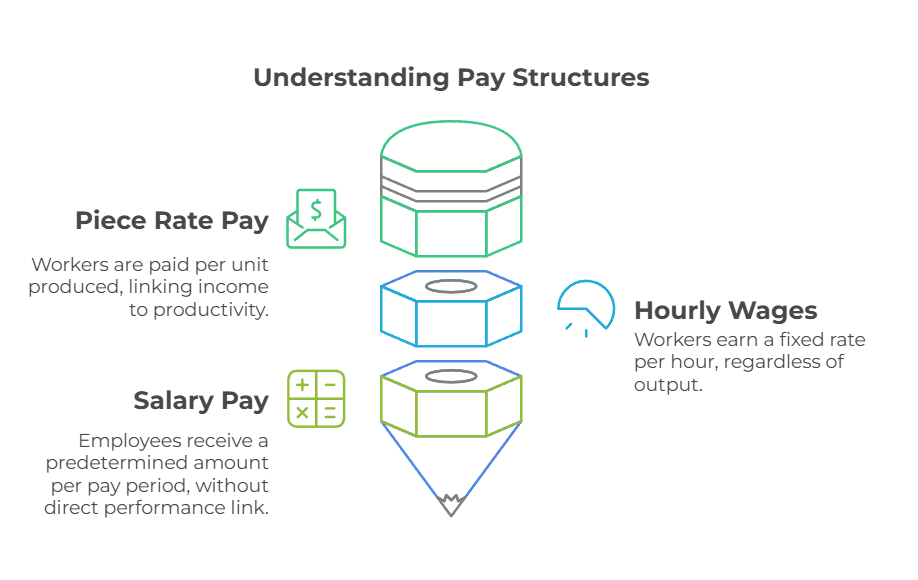
The piece wage system encourages employees to be more productive, but hourly and salary pay offer steady income, which is better for jobs that need a constant level of effort.
Industries Commonly Using Piece Rate Pay
The piece work pay system is used in industries where physical goods are produced, the output can be measured, and the quality of work can be tracked. Manufacturing, agriculture, and construction frequently rely on this system to pay workers based on the number of units produced or tasks completed.
It is also popular in logistics, where couriers and warehouse workers are paid per delivery or package handled. In the service sector, call centers may use piece rate pay for agents handling a certain number of calls. This system works best in jobs where efficiency directly impacts earnings.
Piece rate pay is used when:
- Employee productivity needs to be increased
- Work results depend on individual effort
- The company is willing to set production standards and handle complex payroll calculations
- The work involves uniform production and does not require high qualifications.
Monitor task completion at every stage until the work is finished. Track deviations between actual progress and the plan.
Calculate the cost of finished goods, considering material expenses, production costs, and labor payments.
Identify defects in time, reduce material waste, and increase product profitability.
Types of Piece Rate Pay Structures
Different types of piece rate pay structures suit various industries and work conditions. Here are the most common ones:
Straight Piece Rate Pay
Workers receive a fixed amount for each unit they produce. This system is simple and directly links earnings to productivity.
Differential Piece Rate Pay
Employees earn a higher rate after exceeding a set production target. It encourages workers to maintain high efficiency and rewards extra effort.
Progressive Piece Rate
The pay rate increases after reaching a specific production level. This method motivates workers to continue producing beyond the minimum requirement.
Guaranteed Minimum Wage + Piece Rate
Workers get a base salary along with extra pay for each unit completed. It ensures financial stability and simultaneously promotes higher output.
Time-Based Piece Rate Combination
This system combines hourly or daily wages with piece rate pay. It balances fair compensation for time worked with performance-based incentives.
How to Calculate Piece Rate Pay (With Examples)
Piece rate pay is based on the number of units a worker produces. Below are the key ways to calculate it.
1. Basic Piece Rate Formula
The simplest way to calculate wages under this system is:
Piece Rate Wage = Number of Units Produced × Pay Per Unit
For example, if a worker produces 200 items and earns $5 per item, their total pay is:
200 × $5 = $1,000
2. Including Minimum Wage Compliance
Some workers are paid by the piece but must still earn at least the legal minimum wage. If a worker’s total pay falls below this, the employer must make up the difference.
For example, if a worker produces 50 units at $2 per unit, their pay is $100. If the minimum wage for their hours worked is $150, the employer must pay an extra $50.
3. Overtime Pay for Piecework Employees
Overtime pay applies when a worker exceeds standard hours. Employers can calculate overtime in two ways:
- Find the worker’s average hourly rate based on total earnings and hours worked. Overtime is paid at 1.5 times this rate.
- Pay an additional 50% of the regular piece rate for all units produced during overtime hours.
For example, if a worker’s regular rate is $10 per unit, overtime pay per unit would be $15.
Download our free Excel template for calculating piecework wages using basic formulas
4. Real-World Piece Rate Pay Calculation Examples
- Manufacturing: A textile factory worker assembles 100 garments per shift at $3 per garment. Their total pay is 100 × $3 = $300 per shift.
- Agriculture: A farmworker picks 500 kg of strawberries per week at $0.50 per kg. Their weekly earnings are 500 × $0.50 = $250.
- Construction: A roofer installs 200 shingles per day at $2 per shingle. Their daily wage is 200 × $2 = $400.
|
How to calculate labour costs based on piece rate in Kladana:
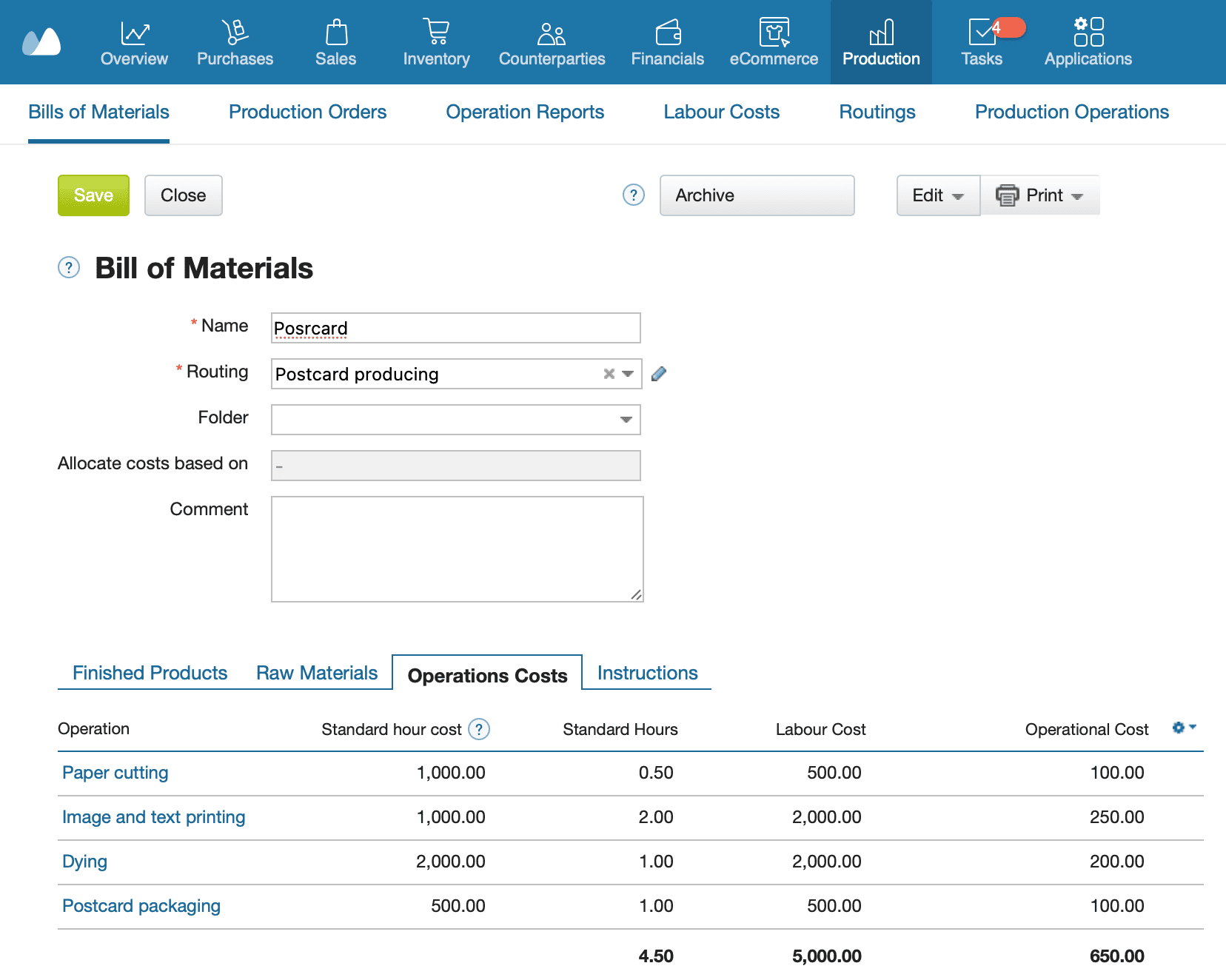
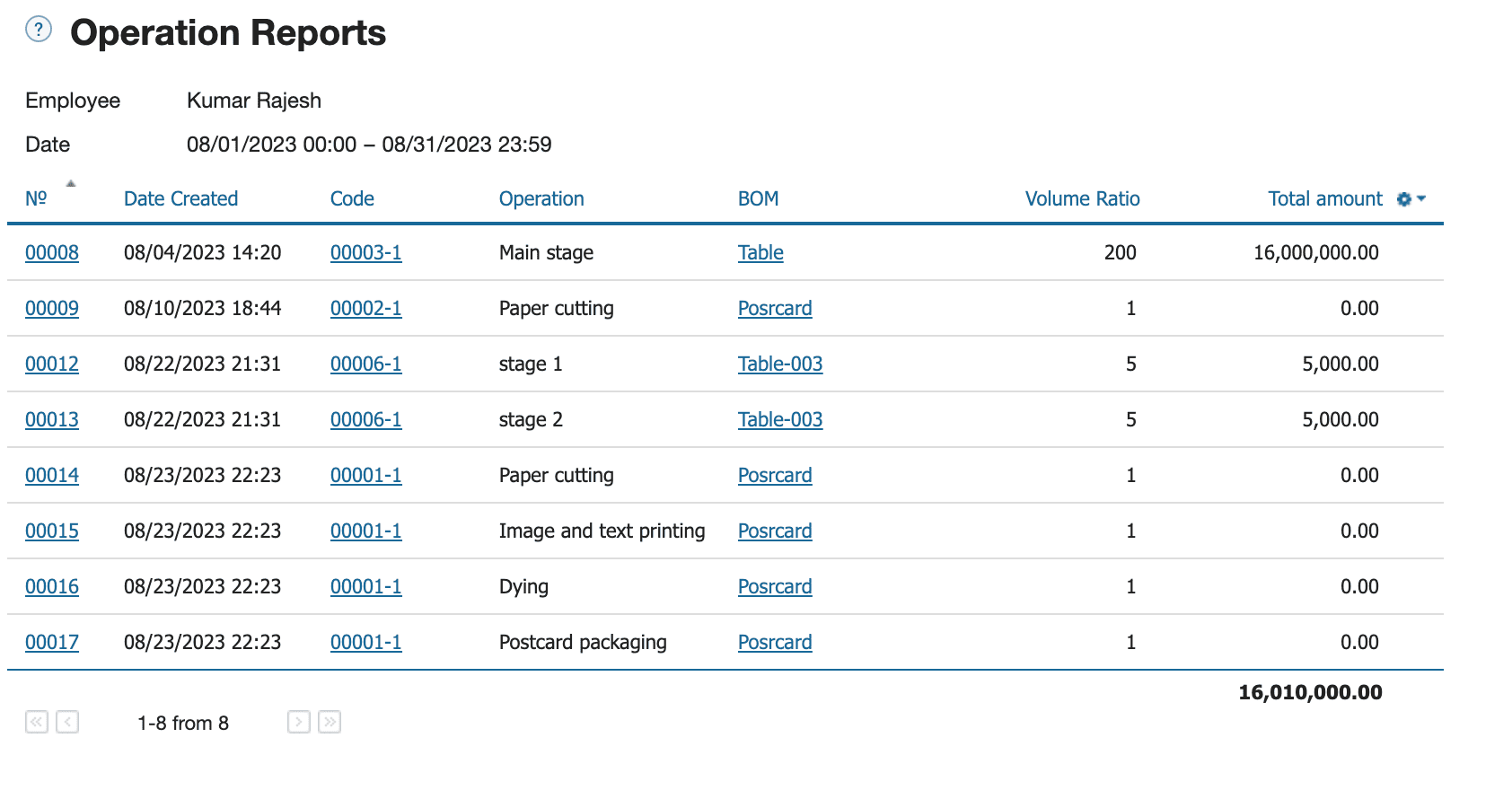
|
Pros and Cons of Piece Rate Pay
Piece rate wages have advantages and disadvantages for both employers and workers. While it can boost productivity and earnings, it also comes with challenges like wage instability and quality concerns. Understanding these factors helps businesses decide if this pay structure fits their needs.
✅ Benefits for Employers & Employees
- Higher productivity — Workers are motivated to produce more since their earnings depend on output.
- Cost control for employers — Businesses pay only for completed work, making labor costs more predictable.
- Higher earning potential — Efficient workers can earn more than those on fixed wages.
- Flexibility — Employers can adjust pay rates based on demand, seasonal work, or production goals.
- Reduced need for supervision — Since workers are paid per unit, they are naturally incentivized to stay on task.
❌ Challenges & Downsides
- Quality issues — Workers may rush to complete tasks, leading to defects or errors.
- Wage inconsistency — Earnings fluctuate based on workload, material availability, and external conditions.
- Legal and compliance risks — Employers must ensure workers meet minimum wage laws and receive proper overtime pay.
- Employee stress — The pressure to produce more can lead to burnout and dissatisfaction.
Best Practices for Implementing a Piece Rate Pay System
A good piece rate pay system can help businesses increase productivity and control costs. To make it work well, companies should focus on fair pay, worker motivation, accurate payroll, and quality control.
1. Setting Fair & Competitive Rates
Pay rates should match industry standards and give workers a fair income. If the rate is too low, workers may quit. If it is too high, costs may increase too much.
Checking and updating pay rates regularly keeps them fair and competitive.
2. Ensuring Worker Motivation & Retention
Workers should see benefits in a piece wage system. Performance bonuses, steady work, and a good work environment help keep employees happy.
Giving workers chances to learn new skills and grow in their jobs can keep them motivated.
3. Using Payroll Software for Accurate Calculations
Tracking piece rate payment manually can be difficult. Payroll software makes sure wages are correct, including overtime and minimum wage rules.
Automated payroll also helps workers trust that they are paid fairly.
4. Tracking Productivity & Quality Control
It is important to measure both output and quality. Clear quality rules help avoid mistakes caused by rushing work.
Proper feedback helps workers improve and keep quality high.
FAQs on Piece Rate Pay
Here are some common questions about piece rate pay to help employers and workers understand how it works.
Is piece rate pay better than hourly pay?
It depends on the job and the worker. Piece rate pay can reward productivity, allowing fast workers to earn more. Hourly pay, on the other hand, provides a stable income. Jobs requiring steady effort over time may be better suited to hourly wages.
Here’s a comparison table between piece rate pay and hourly pay:
| Feature | Piece Rate Pay | Hourly Pay |
Payment Basis |
Based on the number of units produced or tasks completed |
Based on the number of hours worked |
Earnings Potential |
Can be higher if productivity is high |
Fixed rate per hour, regardless of output |
Productivity |
Encourages efficiency and faster work |
May not directly incentivize speed |
Income Stability |
Can fluctuate based on output |
More predictable and stable |
Work Quality |
May decline if workers prioritize speed over accuracy |
More consistent quality, but may lack urgency |
Worker Motivation |
Motivates high performers to produce more |
Provides security but may not push for higher output |
Employer Benefit |
Higher output with potentially lower labor costs |
More control over labor costs and work hours |
Industries Used In |
Manufacturing, agriculture, sales, gig work |
Retail, hospitality, office jobs, administration |
How do you calculate piece rate pay with overtime?
To calculate overtime, first determine the worker’s average hourly rate by dividing total earnings by hours worked. If this rate is below the required overtime rate (usually 1.5 times the minimum wage), the employer must pay the difference.
Can piece rate workers earn below minimum wage?
No. Employers must ensure that total earnings meet at least the minimum wage when divided by hours worked. If earnings fall short, the employer must provide additional pay to meet legal requirements.
What industries commonly use piecework compensation?
Industries like manufacturing, agriculture, construction, and delivery services often use piece rate pay. These jobs involve measurable tasks, making piecework practical.
How do employers ensure quality control with piece rate wages?
Employers set quality standards, conduct regular inspections, and offer bonuses for accuracy. Training workers on best practices also helps maintain high-quality output.
Conclusion — Is Piece Rate Pay Right for Your Business?
Piece rate pay can be a powerful tool for businesses that prioritize productivity and efficiency. It works best in industries where output is easy to measure, such as manufacturing, agriculture, construction, and logistics. This pay system encourages workers to complete more tasks, directly linking earnings to performance. However, it requires strong quality control measures to prevent defects and ensure compliance with wage laws.
For businesses considering piece rate pay, start by setting fair compensation rates, ensuring compliance with minimum wage regulations, and implementing tracking systems to monitor both productivity and quality. Using payroll software can help streamline calculations and maintain accuracy.
If your business relies on measurable output and you want to boost efficiency while maintaining cost control, piece rate pay may be the right solution. With the right approach, it can create a win-win scenario for both employers and employees.
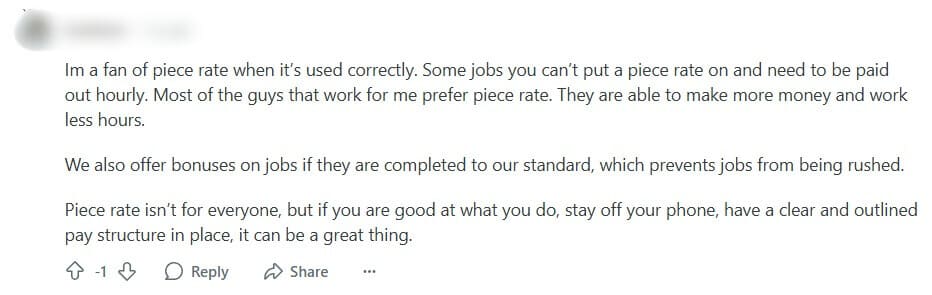
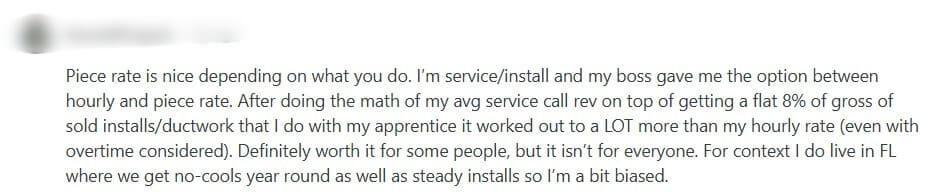
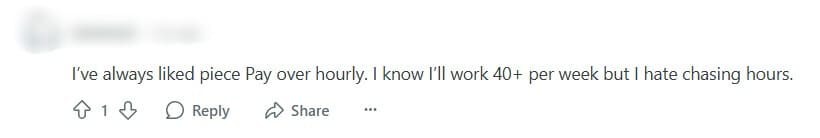
Users Weigh In: Mixed Reactions to Piece Rate Pay
The Reddit community has shared a range of opinions on piece rate pay, with some users praising it while others criticize it. Check out several opinions to help you form your own.

List of resources
- National Bureau of Economic Research — Piece Rate vs. Time Rate: The Effect of Incentives on Earnings
- University of California — High piece-rate wages do not reduce hours worked
- Pubmed National Library of Medicine — A longitudinal study of piece rate and health: evidence and implications for workers in the US gig economy
- International Labour Organization — Piece rate pay and working conditions in the export garment sector