Manufacturing today faces many changes. According to Statista, global manufacturing output is expected to reach $ 50.8 trillion in 2025. Business owners and decision-makers must clearly understand production systems to stay competitive.
A production system in manufacturing integrates technology, processes, people, machines, and materials to produce goods efficiently. Different production systems have unique strengths. Choosing the right one can boost efficiency, save money, and meet customer demands.
This article covers the types, benefits, and examples of production systems to help you understand their role in modern manufacturing.
- What is a Production System in Manufacturing?
- Key Components of a Manufacturing System
- Types of Production Systems
- Benefits of Implementing a Production System
- Production Management Systems
- Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES)
- Operations Management
- Inventory Management
- Advanced Techniques in Production Systems
- Quality Control in Production Systems
- Summary
- Frequently Asked Questions on Production Systems
- List of Resources
What is a Production System in Manufacturing?
A production system is a collection of technology and processes used to produce goods. It integrates various elements such as:
- people
- machines
- materials
- information
These systems are crucial as they fuel the production of commodities and services that people rely on daily, making them an indispensable component of modern life. One example of a production system is the job shop production system, which is suitable for environments with low volume and a wide variety of products, requiring flexibility to meet unique production requirements.
Manufacturing systems, a subset of production systems, consist of integrated equipment and human resources that perform processing and assembly operations on raw materials, parts, or sets of parts. The intricate interaction of these components ensures that manufacturing processes are efficient and productive within a manufacturing production system.
The structure of a production system includes processes, organizational workflow, and output management, all designed to enhance efficiency and reduce costs. At its core, a production system encompasses all methods and resources utilized in manufacturing products. Enhancing efficiency and enabling proactive processes, production systems support companies in achieving their goals and staying competitive.
Kladana ERP is an example of a production management system. Kladana helps you handle everything from raw material purchasing to finished product delivery in a single, browser-based app:
- All-in-One Planning & Inventory: Kladana lets you schedule production stages and ensure the necessary materials are available, all in the same dashboard. This means your production plan is always in sync with your stock levels, preventing surprises and delays.
- Complete Material Tracking: Kladana tracks raw materials, semi-finished goods, and finished products across your operation. You’ll always know what’s in stock (including work-in-progress) and where it’s stored, so nothing falls through the cracks.
- Real-Time Analytics: Kladana gives you real-time insights into production stages and costs — it automatically calculates unit costs based on materials and operations as you work. You can monitor each job’s progress and profitability, allowing you to adjust quickly and keep production efficient.
- Flexible Workflows: You can generate production orders directly from sales orders for made-to-order jobs, or plan batch runs to replenish inventory for made-to-stock needs. The system stays flexible, letting you produce items one step at a time or all in one go — whatever suits your process best.
- Seamless Integration: Kladana isn’t just about production — it ties your whole business together. The platform integrates production with your sales and accounting systems effortlessly, so information flows automatically from one department to the next. When an order comes in or a purchase is made, your production schedule and inventory update instantly. This end-to-end integration means less manual data entry and fewer errors, keeping everyone on the same page.
Key Components of a Manufacturing System
A manufacturing system is composed of several key components that work together to transform raw materials into finished products. These components include:
- production machines,
- material handling systems,
- computer control systems,
- human resources.
Each component plays a critical role in ensuring the smooth operation of the manufacturing process.
✅ Production machines can be manual, semi-automated, or fully automated, each type contributing to different stages of the production process.
✅ Material handling systems are responsible for transporting workpieces between various stations within the manufacturing setup, ensuring that materials move efficiently through the production line.
✅ Computer control systems manage instructions and oversee operations such as scheduling and material handling, enhancing the precision and efficiency of the manufacturing process.
✅ Human resources perform essential tasks that add value and support automated processes, ensuring that the system operates seamlessly.
Types of Production Systems
Production systems can be broadly categorized into two types of production: Intermittent Production Systems and Continuous Production Systems. Each type of production has distinct characteristics and applications, catering to different manufacturing needs and goals.
Intermittent production systems, such as job shops and batch production, operate on a small scale and are characterized by a non-continuous flow of production with high product variety. These systems offer flexibility in production schedules and are ideal for custom orders and small-scale projects.
On the other hand, continuous production systems operate constantly to ensure high efficiency, exemplified by methods like assembly line mass production. These systems are designed for large-scale production based on demand forecasts, providing consistent output and efficiency.
Intermittent Production System
An intermittent production system produces goods based on customer orders and operates on a small scale. This system is characterized by a non-continuous flow of production, allowing for high product variety and customization. The three types of flows in intermittent production systems are Project Production Flow, Jobbing Production Flow, and Batch Production Flow.
Job shop production systems focus on providing custom products that meet specific customer demands, involving skilled labor and manual operations. These systems are ideal for producing unique or varied products that require flexibility in their production processes. Zara’s fast fashion approach relies on short production cycles that enable quick turnaround from design to retail, minimizing excess inventory.
Batch production, another form of intermittent production, involves producing a batch of products before switching to a different type. This method allows manufacturers to produce a diverse range of products while maintaining efficiency. Single-unit production is also a form of intermittent production where the number of product types is diverse but the quantity is not large, and it is usually a non-repeatable process.
Continuous Production System
A continuous production system operates constantly without irregularities, producing goods on a large scale based on demand forecasts rather than customer orders. This system is characterized by a continuous flow of production, ensuring high efficiency and consistent output levels.
In continuous production systems, the manufacturing process runs non-stop to achieve maximum efficiency. These systems can produce a variety of products or a group of products with equipment installed in lines, but they lack flexibility. Assembly line production is a prime example of a continuous production system, where the production process is streamlined to produce large quantities of standardized products.
Continuous production systems are designed to operate at a constant pace, producing items continuously until a full batch is completed or demand dictates otherwise. This approach minimizes downtime and maximizes productivity, making it ideal for industries that require high-volume production.
Benefits of Implementing a Production System
Implementing a production system in manufacturing brings numerous benefits that significantly impact efficiency, quality, and adaptability. Here are some key advantages:
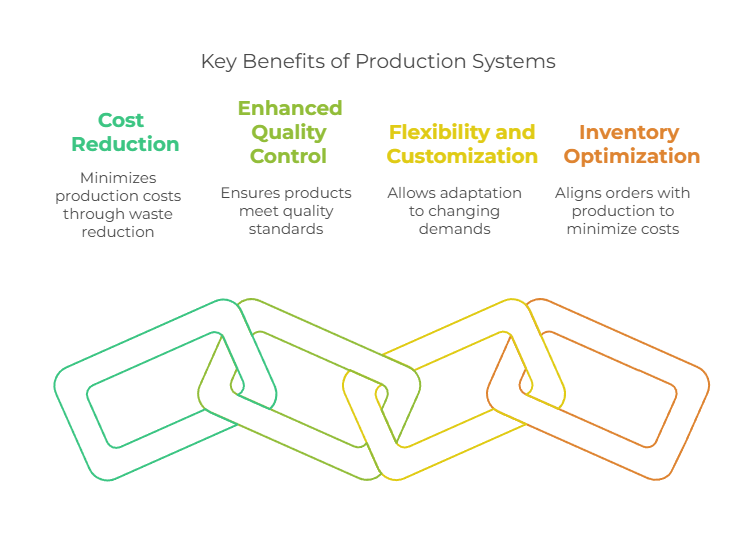
- Cost Reduction: Production systems help in reducing production costs through waste minimization and improved resource utilization. This streamlining of operations ensures businesses can meet production goals cost-effectively.
- Enhanced Quality Control: Production systems enforce standards and quality control measures at each step of the manufacturing process. This ensures that finished products meet required quality standards, boosting the company’s reputation by consistently delivering reliable products.
- Flexibility and Customization: Especially in intermittent production systems, production systems offer greater flexibility and customization. This allows manufacturers to adapt to changing consumer demands and produce a variety of products without significant delays.
- Inventory Optimization: Systems like Just In Time (JIT) align raw material orders with production schedules to minimize inventory costs and enhance responsiveness to customer demands.
Production Management Systems
Production management systems are essential tools that optimize manufacturing processes through automated and data-driven methods. These systems track production data such as Bill of Material, production scheduling, and production costs, ensuring optimal use of resources and providing necessary information for planning and controlling a production management system.
Integrated with Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES), production management systems enhance operational efficiency and data flow. ERP systems focus on overall business operations, while MES systems specialize in monitoring and optimizing production execution, offering tools for tracking real-time production data and improving decision-making.
Functions of Production Management Systems
The main functions of production management systems include:
- Planning: Scheduling production runs to meet demand and ensure efficient utilization of resources.
- Scheduling: Aligning production capacity with market demand and available resources to minimize delays and maximize productivity.
- Resource Allocation: Ensuring optimal use of materials, labor, and equipment to achieve production goals.
Examples of Production Management Systems
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are prime examples of production management systems that integrate core business processes across various departments, providing real-time data and improving operational efficiency. These systems automate routine tasks, enhance cross-functional collaboration, and provide real-time production analytics, leading to better decision-making and resource management.
Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) facilitate real-time monitoring and control of the production process, ensuring effective scheduling and quality management. These systems link enterprise resource planning with operational activities, offering enhanced visibility and traceability throughout the production cycle.
Other examples include Material Requirements Planning (MRP) systems that manage inventory and production schedules to ensure optimal resource use. These production management systems are crucial for manufacturers aiming to enhance productivity, reduce waste, and ultimately improve profitability.
Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES)
A Manufacturing Execution System (MES) is a software-based solution that plays a pivotal role in modern manufacturing by tracking and controlling the production process in real-time. MES provides manufacturers with real-time data on production processes, enabling them to make informed decisions and optimize their operations effectively.
By integrating with other systems such as Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Supply Chain Management (SCM), MES offers a comprehensive view of the entire production process. This integration ensures seamless data flow and coordination across different departments, enhancing overall efficiency.
One of the key benefits of MES is its ability to improve quality, reduce waste, and increase efficiency. By providing real-time monitoring and control of production processes, MES helps manufacturers identify and address issues promptly, ensuring that production runs smoothly. Additionally, MES offers historical data and analytics, enabling manufacturers to identify trends and areas for improvement, further optimizing their operations.
In summary, MES is an indispensable tool in the manufacturing industry, providing real-time insights and control that drive efficiency, quality, and continuous improvement.
Operations Management
Operations management is the process of planning, organizing, and supervising the production of goods and services. It involves the management of resources such as raw materials, labor, and equipment to ensure that production processes run smoothly and efficiently.
A key aspect of operations management is the management of production processes, which includes quality control, inventory management, and supply chain management. The goal of operations management is to produce goods and services that meet customer requirements while minimizing costs and maximizing efficiency.
To achieve these goals, operations management employs various techniques such as lean manufacturing, total quality management, and just-in-time production. Lean manufacturing focuses on minimizing waste and maximizing value, while total quality management emphasizes continuous improvement and customer satisfaction. Just-in-time production aims to reduce inventory levels and improve efficiency by producing goods only as needed.
In essence, operations management is crucial for ensuring that manufacturing processes are efficient, cost-effective, and capable of meeting customer demands.
Inventory Management
Inventory management is the process of managing the storage, handling, and movement of goods and materials within a production system. It involves tracking inventory levels, including raw materials, work-in-progress, and finished goods, to ensure that production processes run smoothly.
Effective inventory management also involves managing inventory costs, such as the cost of holding inventory, ordering inventory, and dealing with stockouts. The goal is to maintain optimal inventory levels while minimizing costs and maximizing efficiency.
Various techniques are used in inventory management to achieve these goals. Just-in-time production, for example, minimizes inventory levels by producing goods only as needed. Economic order quantity helps determine the optimal order size to minimize costs, while inventory optimization uses data and analytics to maintain the right balance of inventory.
In summary, inventory management is a critical component of a production system, ensuring that materials are available when needed while keeping costs under control.
Advanced Techniques in Production Systems
Modern manufacturing leverages advanced techniques like lean manufacturing and Just In Time (JIT) production to optimize production processes and enhance efficiency. These techniques focus on minimizing waste, maximizing capacity, and improving responsiveness to market changes.
Lean manufacturing principles, for example, aim to create value for customers by continuously improving processes and reducing resource wastage. JIT production, on the other hand, minimizes inventory costs by delivering materials only as needed, aligning production schedules with customer demand.
Lean Manufacturing
Lean manufacturing focuses on maximizing value by minimizing waste across all production activities. The first step in creating value for the customer according to Lean principles is identifying what is considered valuable to the customer. Continuous improvement is essential in lean manufacturing to enhance efficiency and productivity.
One key principle of lean manufacturing is to continuously improve processes to deliver greater value. The objective of Lean Line Design (LLD) is to create flexible work systems that can adapt to changes in customer consumption while reducing waste and ensuring consistent productivity.
Companies like Boeing have successfully improved their assembly lines by integrating lean manufacturing principles, resulting in reduced production time and costs. Nike’s adoption of a demand-driven supply chain model, inspired by lean principles, has enhanced its responsiveness to market needs, leading to improved sales performance.
These examples highlight the transformative impact of lean manufacturing on production efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Just In Time Production (JIT)
Just In Time (JIT) production is a system that delivers materials only as needed, in small quantities. The primary purpose of JIT production is to minimize inventory while fulfilling customer requirements effectively. This approach reduces inventory costs and improves efficiency, ensuring that resources are used optimally.
A midsize food services company adopted a JIT strategy, successfully reducing food waste by 20% and enhancing customer satisfaction through improved inventory management. Toyota’s JIT production technique has also significantly minimized inventory costs and improved efficiency and productivity in their manufacturing processes.
By aligning production schedules with customer demand, JIT production systems ensure that finished products are produced cost-effectively and delivered on time, enhancing overall production flexibility and customer satisfaction.
Quality Control in Production Systems
Quality control is a crucial part of the manufacturing process, ensuring that finished products meet required quality standards. Establishing a quality control system helps maintain high-quality output and boosts the company’s reputation by consistently delivering reliable products.
Production management software can significantly enhance product quality by enforcing standards and quality control measures at each step of the manufacturing process. These systems facilitate real-time monitoring of production processes, allowing for timely adjustments and optimization of performance.
Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) play a vital role in tracking production processes from raw materials to finished goods, providing valuable data for decision-making and quality assurance. Lean practices can also lead to improved product quality and reduced operational costs, making quality control an integral part of successful production systems.
Summary
Throughout this exploration of production systems in manufacturing, we’ve delved into the various types, key components, benefits, and advanced techniques that define efficient manufacturing operations. Understanding what a production system is and how it integrates people, machines, materials, and information is crucial for any manufacturing business aiming to improve efficiency and product quality.
We’ve detailed the components of a manufacturing system, from production machines and material handling systems to computer control systems and human resources, highlighting their roles in creating a cohesive and efficient manufacturing process. By implementing well-designed production systems, businesses can significantly reduce costs, enhance quality control, and adapt to market changes more effectively.
Advanced techniques like lean manufacturing and Just In Time (JIT) production further optimize production processes, minimize waste, and improve responsiveness to customer demands. Quality control systems ensure that finished products meet required standards, maintaining high-quality output and boosting company reputation. As we conclude, it’s clear that a robust production system is the backbone of successful manufacturing, driving operational excellence and organizational success.
Frequently Asked Questions on Production Systems
What is the purpose of Just In Time Production (JIT)?
Just In Time (JIT) production is a strategy that involves producing goods just in time to meet customer demand. The primary purpose of JIT production is to minimize inventory levels, reduce waste, and improve efficiency.
JIT production operates on the principle of producing goods in small batches, just in time to meet customer demand. This approach contrasts with traditional production methods that rely on forecasted demand and large inventory levels. By using a pull system, where production is triggered by actual customer demand, JIT production ensures that resources are used optimally and waste is minimized.
The benefits of JIT production are significant. Reduced inventory levels mean lower holding costs and less risk of obsolescence. Improved quality results from the focus on producing only what is needed, reducing the likelihood of defects. Increased efficiency is achieved through streamlined production processes and better alignment with customer demand.
In conclusion, JIT production is a powerful strategy for manufacturers looking to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve product quality by aligning production closely with customer needs.
What is the significance of a flow-oriented layout (FOL) in production planning?
The significance of a flow-oriented layout (FOL) in production planning lies in its ability to minimize waste, enhance unit flow, and reduce cycle time, ultimately leading to increased efficiency in the production process. By optimizing these factors, FOL supports streamlined operations and improved productivity.
What does a production management system include?
A production management system includes methods, procedures, and structured arrangements for collecting inputs and delivering final products to the market efficiently. This ensures an organized process that enhances productivity and quality control.
What are the types of production management techniques mentioned?
The types of production management techniques include job shop production, batch production, mass production, and continuous production. Each method is tailored to specific manufacturing needs and scales.
What is the objective of the Lean Line Design (LLD)?
The objective of Lean Line Design (LLD) is to establish adaptable work systems that minimize waste while maintaining consistent productivity and responsiveness to customer demand. This approach ultimately aims to enhance efficiency and effectiveness in operations.
How does lean manufacturing contribute to production efficiency?
Lean manufacturing contributes to production efficiency by eliminating waste, optimizing processes, and focusing on value creation for the customer. It emphasizes continuous improvement and aims to streamline operations, resulting in higher productivity and reduced operational costs.
What role does inventory management play in a production system?
Inventory management plays a critical role in a production system by ensuring that raw materials, work-in-progress, and finished goods are available when needed. Effective inventory management minimizes holding costs and stockouts, optimizing production flow and meeting customer demands.
How do Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) enhance production quality?
Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) enhance production quality by providing real-time monitoring and control of production processes. MES ensures that quality standards are met by tracking production data, identifying potential issues early, and facilitating timely interventions.
What is the impact of advanced technologies on production systems?
Advanced technologies impact production systems by increasing automation, improving precision, and enabling data-driven decision-making. These technologies enhance efficiency, reduce errors, and allow for greater flexibility and customization in manufacturing processes.
How do production systems adapt to changing consumer demands?
Production systems adapt to changing consumer demands by incorporating flexible manufacturing processes, such as job shop production and batch production. These systems allow manufacturers to quickly adjust production schedules and output to meet evolving market needs and customer preferences.
List of Resources
- Statista — Manufacturing Worldwide